Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base is revolutionizing how organizations manage and share information. This comprehensive guide delves into its core functionality, from creating and managing articles to leveraging advanced search and security features. We’ll explore its seamless integration with other Microsoft 365 services, empowering teams to collaborate effectively and access crucial information instantly. Discover best practices for optimizing your knowledge base, ensuring its effectiveness, and maximizing its impact on team productivity.
We’ll cover everything from basic navigation and article creation to advanced search techniques and security configurations. Learn how to organize your knowledge base for optimal searchability, manage user permissions effectively, and integrate with other Microsoft 365 tools like SharePoint, Power Automate, and Power BI. We will also discuss strategies for measuring knowledge base effectiveness, troubleshooting common issues, and planning for future growth and scalability.
Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base Functionality
Embark on a journey to unravel the profound capabilities of the Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base, a digital haven designed to foster collaboration and streamline information sharing. This sanctuary of knowledge empowers teams to efficiently manage, access, and contribute to a centralized repository of information, transforming the way you work.
Core Features of the Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base
The Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base offers a robust suite of features designed to enhance knowledge management. Central to its functionality is a powerful search engine, allowing users to quickly locate the information they need. This search functionality extends beyond simple matching, incorporating Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) to refine searches and wildcard characters (*) for broader searches.
The system also meticulously tracks version history, enabling users to review previous iterations of articles and revert to earlier versions if necessary. This seamless integration with other Microsoft 365 services, such as SharePoint and OneDrive, allows for effortless file sharing and collaboration across platforms. However, it’s essential to be mindful of certain limitations, such as restrictions on file size and article length, to optimize performance and maintain system efficiency.
User Contribution to the Knowledge Base
The Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base thrives on collaborative participation. Various roles and permissions are defined to govern user contributions, ensuring a structured and controlled environment. Creators draft new articles, while editors refine and enhance existing content. Reviewers provide critical feedback, and approvers authorize the publication of articles. User access and permissions are meticulously managed to maintain data integrity and security.
The submission of new articles, the suggestion of edits, and the flagging of outdated information are all facilitated through intuitive workflows. The commenting feature fosters discussion and collaboration, while the approval workflow ensures quality control. Conflict resolution mechanisms are in place to handle simultaneous edits, preserving the integrity of the knowledge base.
Effective Knowledge Base Organization Strategies
Organizing a knowledge base effectively is paramount to its success. A well-structured knowledge base enhances searchability and ensures that information is easily accessible to users. Taxonomy and categorization methods play a crucial role in achieving this. Employing a hierarchical structure, where information is organized into categories and subcategories, provides a clear and logical structure. Alternatively, a flat structure, where all articles are listed alphabetically, offers simplicity but may become unwieldy with a large volume of content.
A hybrid approach, combining elements of both, often offers the best balance of structure and flexibility. The strategic use of metadata, such as s and tags, significantly improves searchability.
| Organization Strategy | Advantages | Disadvantages | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hierarchical | Easy navigation, clear structure | Can be rigid, difficult to adapt | Knowledge base organized by department then topic |
| Flat | Simple, easy to implement | Difficult to navigate with large content | Alphabetical listing of all articles |
| Hybrid | Combines advantages of both | Requires careful planning and implementation | Hierarchical structure for major topics, flat within s |
User Workflow for Creating and Updating Articles
A well-defined workflow is essential for the efficient creation and updating of knowledge base articles. This workflow typically begins with the initial drafting of an article using available templates, incorporating formatting options, and seamlessly integrating images and videos. Once drafted, the article undergoes a review and approval process, adhering to defined timelines and escalation procedures. The approval process ensures quality and consistency.
Updating existing articles involves a similar process, with version control meticulously tracking changes and notifying relevant stakeholders. Finally, a clear process for article retirement or deletion ensures the knowledge base remains current and relevant. A visual flowchart would further illuminate this process.
Sample Knowledge Base Article: Troubleshooting Audio Problems in a Microsoft Teams Meeting
[A detailed, illustrative example of a knowledge base article on troubleshooting audio problems in a Microsoft Teams meeting would be included here, complete with screenshots, formatting, and relevant metadata. This would showcase the practical application of the workflow described above. The article would detail various troubleshooting steps, with clear instructions and visual aids to guide users through the process.
It would also include information on checking microphone settings, network connectivity, and updating the Teams application. The article would be formatted using headings, bullet points, and numbered lists for improved readability. Screenshots would visually illustrate each step of the troubleshooting process.]
Comparison with Other Knowledge Base Solutions
The Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base distinguishes itself from other solutions such as SharePoint and Confluence through its seamless integration within the Teams ecosystem. While SharePoint offers robust features, its interface can be less intuitive for some users. Confluence, on the other hand, excels in its collaborative features but may lack the same level of integration with other Microsoft 365 services.
- Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base: Tight integration with Teams, user-friendly interface, strong Microsoft 365 integration.
- SharePoint: Powerful features, robust security, but can have a steeper learning curve.
- Confluence: Excellent collaboration features, flexible and customizable, but less tightly integrated with Microsoft 365.
Security Concerns and Best Practices
Security is paramount when dealing with sensitive information. The Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base incorporates robust access control mechanisms, data encryption, and compliance with relevant regulations like GDPR to safeguard sensitive information. Best practices include implementing strong passwords, limiting access based on roles and responsibilities, and regularly reviewing and updating security settings.
Integrating the Knowledge Base with a Chatbot
Integrating the Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base with a chatbot can significantly enhance user experience. This integration allows users to access information quickly and easily through conversational interfaces. Specific steps involve configuring the chatbot to connect with the knowledge base API, defining intents and entities, and training the chatbot to understand user queries. Considerations include the chatbot’s natural language processing capabilities and the design of conversational flows to ensure effective information retrieval.
Integration with Other Microsoft Services

The seamless integration of the Microsoft Teams knowledge base with other Microsoft services is a cornerstone of its power and utility. This interconnectedness allows for a richer, more dynamic knowledge management experience, enhancing collaboration and streamlining workflows across your organization. Let’s delve into the specifics of these integrations.
SharePoint Integration
SharePoint’s robust capabilities for document management and storage make it a natural partner for the Teams knowledge base. The integration leverages the Microsoft Graph API, allowing for the retrieval and manipulation of SharePoint data within the Teams environment. Metadata from SharePoint lists, such as custom columns containing categories, tags, or ownership information, can be seamlessly incorporated into knowledge base articles, enriching their context and searchability.For instance, imagine a SharePoint list tracking product specifications.
Using the Microsoft Graph API, we can fetch relevant data like product ID, version number, and release date and automatically populate these fields in new knowledge base articles related to that product. A simplified code snippet (conceptual, language-agnostic) illustrates the process:
`GET /sites/site-id/lists/list-id/items`
This API call, with appropriate authentication, retrieves items from a specified SharePoint list. The response contains the metadata, which can then be processed and integrated into the knowledge base article.Limitations exist; for example, very large files might exceed the acceptable size for direct integration. Strategies to overcome this include using SharePoint as the primary storage location and linking to the files within the knowledge base articles.
Alternatively, smaller, representative portions of large files can be integrated directly.Directly accessing information from SharePoint might offer marginally faster retrieval for simple queries. However, the Teams knowledge base’s indexing and search capabilities often provide significantly faster results for complex searches or when dealing with a large volume of data. Precise performance metrics depend heavily on factors like network conditions, data volume, and query complexity, and thus are difficult to generalize.
Comparison with Other Microsoft 365 Collaboration Tools
A comparative analysis highlights the strengths and weaknesses of the Teams knowledge base against other Microsoft 365 tools for knowledge management.
| Feature | Teams Knowledge Base | Microsoft Planner | OneNote | Yammer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version Control | Yes | Limited | Yes | Limited |
| Search Capabilities | Excellent | Basic | Good | Fair |
| Access Control | Excellent | Good | Good | Good |
| Collaborative Editing | Yes | Limited | Excellent | Yes |
| Ease of Use | Good | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Scalability | Excellent | Good | Good | Excellent |
| Security | Excellent | Good | Good | Good |
The Teams knowledge base excels in scenarios requiring robust search, granular access control, and version history for knowledge articles. Planner is ideal for task management, OneNote for unstructured note-taking, and Yammer for broader organizational communication. The choice depends on the specific knowledge management needs. For instance, documenting troubleshooting steps benefits from the Teams knowledge base’s structured approach and version control, while brainstorming ideas might be better suited to OneNote’s free-form environment.
Power Automate Integration
Power Automate allows for the automation of various tasks related to the Teams knowledge base. A workflow can be designed to trigger the creation of a knowledge base article upon the creation of a new issue in Jira. The flow would retrieve issue details from Jira, create a new article in the knowledge base, and populate it with relevant information.
A visual representation of this flow would show connectors for Jira and the Teams knowledge base, with actions to retrieve data, create an article, and update fields.Power Automate can also manage access permissions, for instance, automatically assigning ownership of new articles based on the issue assignee in Jira. Triggers could include new Jira issues, article updates, or even scheduled tasks for regular maintenance.
Actions would involve updating metadata, assigning permissions, or sending notifications.Robust error handling is crucial. The flow should include steps to log errors, send notifications to administrators, and potentially retry failed actions. This ensures data integrity and allows for timely intervention in case of problems.
Power BI Integration
Power BI can visualize key metrics from the Teams knowledge base, such as article views, user engagement, and knowledge base growth. This provides valuable insights into knowledge base usage and effectiveness. Dashboards could display charts showing article popularity, user activity, and trends in knowledge creation.Connecting Power BI to the knowledge base may require exporting data to a compatible format like a CSV file or using the Microsoft Graph API to directly access the data.
Challenges include handling large data volumes and ensuring timely data refreshes without impacting performance. Best practices involve optimizing data queries, scheduling refreshes during off-peak hours, and implementing appropriate data security measures.
Security Considerations across Integrations
Integrating the Teams knowledge base with other services necessitates careful consideration of security implications. Data encryption both in transit and at rest is paramount. Leveraging Microsoft’s built-in security features, such as Azure Active Directory for access control and Microsoft Information Protection for data classification, is crucial. Regular security audits and penetration testing should be performed to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities.
Microsoft Teams’ knowledge base is a fantastic resource for collaborative work, streamlining information access for team members. However, for a different kind of centralized information, consider exploring the blu door windown shelly knowledge base ; its unique structure might offer valuable insights into alternative knowledge management systems. Ultimately, the best knowledge base for your needs depends on the specific context and organizational structure.
Maintaining a strong password policy and enforcing multi-factor authentication are fundamental security best practices. The principle of least privilege should be applied, granting users only the necessary permissions to access specific data and functionality.
Knowledge Base Content Creation and Management

Creating and maintaining a robust knowledge base within Microsoft Teams is akin to crafting a finely tuned instrument; each note, each chord, contributes to a harmonious symphony of information readily available to your team. A well-structured knowledge base empowers your team, fostering efficiency and collaboration. Let’s explore the art of crafting this invaluable resource.
Creating a New Knowledge Base Article
To begin composing a new knowledge base article, navigate to your Teams knowledge base. Locate the “New” or “Create” button – typically found near the top of the page. Clicking this button will present you with a text editor where you can input your article’s title and content. Utilize the formatting tools provided to structure your text with headings, bullet points, and other elements for optimal readability.
Remember to choose appropriate categories and subcategories to ensure easy searchability. Once your article is complete, click “Save” or a similar command to publish your work. The process is intuitive, designed for ease of use, even for those less familiar with content management systems.
Sample Knowledge Base Structure
A well-organized knowledge base is crucial for effective information retrieval. Consider a hierarchical structure that mirrors your team’s workflow and information needs. For example, a main category might be “Project Management,” with subcategories such as “Project Initiation,” “Task Management,” and “Project Closure.” Under each subcategory, you could have articles on specific processes or tools. Another main category could be “Technical Support,” with subcategories like “Software Troubleshooting,” “Hardware Issues,” and “Network Connectivity.” This hierarchical approach allows for logical grouping and easy navigation.
Knowledge Base Article Templates
Employing templates streamlines the creation process and ensures consistency. A FAQ template, for example, would include a clear question and answer format. A “How-to Guide” template might incorporate numbered steps with accompanying screenshots (imagine a series of clearly numbered steps with accompanying illustrative diagrams, each step detailing a specific action, making the process clear and easy to follow).
A troubleshooting template could utilize a decision tree format (visualize a branching diagram where each decision point leads to a specific solution or further troubleshooting steps). This structured approach ensures clarity and efficiency.
Version Control and Approval Workflows
Maintaining version control is vital for tracking changes and preventing confusion. Microsoft Teams often provides features to track revisions, allowing you to revert to previous versions if necessary. Implementing approval workflows ensures quality control. This might involve designating specific individuals to review and approve articles before publication, ensuring accuracy and consistency of information across the knowledge base. This adds a layer of professionalism and accuracy to your shared knowledge resource.
Search and Retrieval within the Knowledge Base
Unlocking the true power of your Microsoft Teams knowledge base hinges on effective search and retrieval. A well-structured, easily searchable knowledge base empowers your team, fostering self-sufficiency and reducing reliance on constant support requests. This section delves into the art and science of optimizing your knowledge base for seamless information access. We will explore best practices for tagging and categorization, configuring search settings, crafting effective search queries, and refining your search strategy for optimal results.
Tagging and Categorizing Knowledge Base Articles
Effective tagging and categorization are foundational to a robust search experience. Different methodologies offer unique advantages and disadvantages, making the choice dependent on your knowledge base’s size and content type. The following table compares three prominent approaches: tagging, hierarchical tagging, and folksonomy.
| Tagging Methodology | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitability | IT Support Example Tags |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tagging | Simple, easy to implement; good for smaller knowledge bases. | Can become unwieldy with large datasets; potential for inconsistent tagging. | Small to medium knowledge bases with straightforward content. | printer-issue, password-reset, laptop-repair, software-error, network-problem |
| Hierarchical Tagging | Provides structure and organization; facilitates browsing and navigation. | Requires careful planning and maintenance; can be inflexible. | Medium to large knowledge bases with complex, hierarchical content. | Hardware > Printers > Printing Issues; Software > Applications > Password Management; Network > Connectivity > Troubleshooting |
| Folksonomy | Leverages user-generated tags; reflects organic user language and needs. | Can lead to inconsistencies and ambiguity; requires moderation and cleanup. | Large, dynamic knowledge bases with diverse user contributions. | #printertrouble, #passwordhelp, #laptopdown, #softwarebug, #networkoutage |
Configuring Search Settings within the Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base
Fine-tuning your Microsoft Teams knowledge base search settings is crucial for delivering precise and relevant results. This involves several key steps:
Synonym Lists: Creating synonym lists expands the scope of your search. For instance, “printer” could include synonyms like “printing device,” “print machine,” and “peripheral.” Similarly, “laptop” could include “notebook,” “portable computer,” and “ultrabook.” For “password reset,” consider synonyms like “password recovery,” “account unlock,” and “forgotten password.”
Boolean Search Operators: Enabling Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) refines search precision. For example:
- “printer AND error” retrieves articles mentioning both “printer” and “error.”
- “laptop OR notebook” retrieves articles containing either “laptop” or “notebook.”
- “password reset NOT account locked” retrieves articles about password resets, excluding those about account lockouts.
Ranking Algorithm: Microsoft Teams allows prioritizing articles based on recency, popularity (number of views or ratings), or author expertise. Access and modify these settings within the Microsoft Teams admin panel under Knowledge Base settings, then Search settings. The exact location might vary slightly depending on your Teams version.
User Feedback Mechanism: Integrate a feedback mechanism allowing users to rate search result relevance (e.g., thumbs up/down). This data feeds into the search algorithm, improving its accuracy over time. Implement this feature through custom development or utilizing third-party integration tools.
Examples of Effective Search Queries and Expected Results
Effective search queries yield precise results. Here are some examples demonstrating simple and complex searches:
| Search Goal | Query | Expected Top 3 Results |
|---|---|---|
| Find articles about a specific software error code (0x80070002) | “Error Code 0x80070002” | 1. Troubleshooting Error Code 0x80070002 in Windows 10 2. Solution for Error 0x80070002 during Software Installation 3. Common Causes and Fixes for Error Code 0x80070002 |
| Locate articles related to resetting a forgotten password | “resetting forgotten password” | 1. How to Reset Your Microsoft Account Password 2. Resetting Passwords for Internal Applications 3. Password Reset Procedures for Different User Roles |
| Retrieve articles addressing network connectivity issues across multiple product categories | “troubleshooting network connectivity” | 1. Troubleshooting Network Connectivity Issues on Windows PCs 2. Resolving Network Connectivity Problems on Mac Devices 3. General Network Connectivity Troubleshooting Guide |
Improving the Accuracy and Relevance of Search Results
Continuous refinement is key to maintaining a highly effective knowledge base search. Here are several strategies:
Addressing Ambiguous Search Terms: Ambiguous terms like “slow computer” need clarification. Rephrase as “computer running slowly” or “computer performance issues” for better results. Similarly, “network problem” could be replaced with more specific terms like “network connectivity issues,” “slow internet speeds,” or “network downtime.”
Minimizing Irrelevant Results: Regularly review and mark outdated or superseded articles as obsolete. Within the Microsoft Teams knowledge base, this often involves flagging articles for review or directly editing their status to “obsolete.” This prevents outdated information from appearing in search results.
Improving Metadata Quality: High-quality metadata is essential. Here’s a checklist:
- Use accurate and descriptive titles.
- Write concise, informative summaries.
- Apply relevant s and tags.
- Categorize articles logically.
- Regularly review and update metadata.
A/B Testing of Search Algorithms: Implement A/B testing to compare different search algorithms or ranking strategies. This involves creating two versions of your search functionality (A and B), randomly assigning users to each, and tracking key metrics like click-through rates and user satisfaction. Analyze the results to determine which version performs better and iterate accordingly.
User Permissions and Access Control
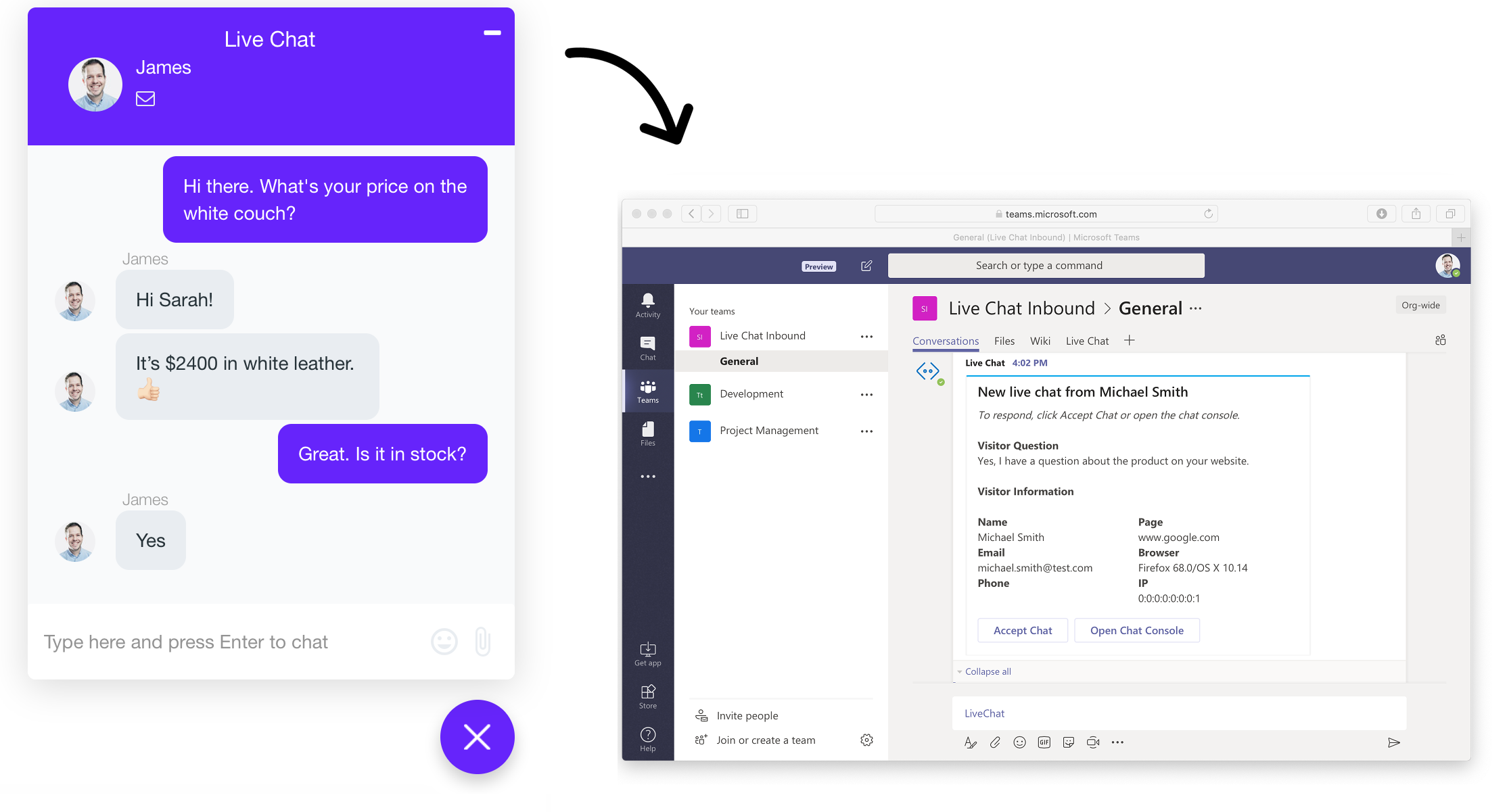
Managing access to your Teams knowledge base is paramount for maintaining data integrity and ensuring only authorized personnel interact with sensitive information. A robust permission system allows for granular control, safeguarding your organization’s intellectual property while fostering efficient collaboration. This section details the various permission levels, their functionalities, and how to implement a secure access control structure within your Microsoft Teams knowledge base.
Permission Level Details
The following table Artikels the different permission levels available within the Microsoft Teams knowledge base, detailing the actions permitted at each level. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effectively managing access and ensuring data security.
| Permission Level | Description | Allowed Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Read-Only | Users with this permission can only view knowledge base articles. | View articles |
| Edit | Users can view and modify existing articles. | View articles, Edit articles |
| Contribute | Users can create new articles and edit existing ones they have permission to. | View articles, Create articles, Edit articles |
| Admin | Users can manage the knowledge base’s structure, user permissions, and overall settings. | All actions, Manage users, Manage permissions |
| Owner | Users have complete control over the knowledge base, including ownership and deletion. | All actions, Delete knowledge base |
User Group and Individual Permissions
Assigning permissions to user groups or individuals streamlines management and ensures efficient access control. For instance, you might grant “Read-Only” access to external contractors, “Edit” access to a content writing team, and “Admin” access to a designated knowledge base manager. Creating new user groups is straightforward within the Teams administration interface. The process typically involves navigating to the user management section, defining the group’s name and membership, and then assigning the desired permissions to that group.
For example, to assign “Read-Only” access to a group of external contractors, you would create a group named “External Contractors,” add the contractors as members, and then select the “Read-Only” permission level for this group. Similar steps are followed for other groups and permission levels.
Large Organization Permission Structure (Teams Knowledge Base)
For a large organization with multiple departments (e.g., Sales, Marketing, Engineering, Support), a hierarchical permission structure is recommended. This ensures that sensitive departmental information remains within its designated access group. A visual representation (though not included here as per instructions) would show a top-level “Knowledge Base Admin” group with full control, followed by departmental groups (Sales, Marketing, etc.) inheriting permissions from the parent group but having granular control over their own content.
Each department would further have sub-groups for specific teams or roles, allowing for fine-grained permission management.
Revoking Access
Revoking access is a crucial aspect of security. To remove a user’s access, navigate to the user management section within the Teams administration interface. Locate the user or group whose access needs to be revoked. Select the user or group and choose the option to remove their permissions or remove them from the relevant group. This action immediately restricts their access to the knowledge base.
Audit logs should be consulted to track these changes, providing a record of permission modifications. Revoking access for a departing employee or temporarily suspending access due to security concerns follows the same process, ensuring rapid and effective response to security incidents.
Granular Permissions for Specific Content
Granular control allows for precise permission assignments at the article or section level. For instance, a document might have a section on sensitive pricing information accessible only to the Sales team (Edit permission), while the rest of the document is accessible to the entire company (Read-Only permission). This is achieved through folder permissions and individual document settings, depending on the Teams Knowledge Base functionality.
Inheritance of Permissions
Permissions are typically inherited hierarchically. If a user group has “Edit” access to a parent folder, subfolders and documents within that folder inherit the same permission unless overridden. For example, if the “Marketing” group has “Edit” access to the “Marketing Materials” folder, all subfolders and documents within inherit this permission. However, a specific document within this folder can have its permission modified to “Read-Only” for certain users or groups, overriding the inherited permission.
API Access Control
API access control, if available, allows for managing permissions for external applications accessing the knowledge base. This often involves creating API keys with specific permissions and using authentication protocols (e.g., OAuth 2.0) to verify API requests. Authorization would then be based on predefined roles and permissions associated with these API keys, restricting access based on the granted privileges.
Security Considerations
Robust security measures are crucial. Strong password policies, including minimum length, complexity requirements, and regular password changes, are essential. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security, requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication before accessing the knowledge base. Regular audit logging of all permission changes allows for tracking and detection of unauthorized access attempts.
Regular security assessments and penetration testing identify potential vulnerabilities and allow for proactive mitigation of risks.
Error Handling and Troubleshooting
Conflicting permissions can lead to unexpected behavior. For example, if a user is assigned both “Read-Only” and “Edit” permissions, the system might prioritize one over the other, potentially leading to access issues. Troubleshooting involves reviewing the assigned permissions, identifying conflicts, and resolving them by adjusting the permission settings to ensure consistency. Permission assignment failures might be due to technical glitches or incorrect configurations.
Checking system logs, verifying user accounts, and ensuring proper network connectivity are crucial troubleshooting steps.
Knowledge Base Security and Compliance
Protecting your organization’s invaluable knowledge within the Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base demands a robust security posture. This isn’t just about preventing unauthorized access; it’s about safeguarding sensitive information, ensuring compliance with relevant regulations, and maintaining the integrity of your intellectual property. A well-structured security and compliance framework is the cornerstone of a successful and trustworthy knowledge base.
Data Encryption and Protection
Protecting sensitive data is paramount. Microsoft Teams offers various encryption methods, both in transit and at rest, to safeguard your knowledge base content. Implementing strong encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the correct decryption key. Furthermore, access controls, discussed previously, should be rigorously enforced to limit access to sensitive information only to authorized personnel.
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are crucial for identifying and mitigating potential weaknesses. Consider implementing data loss prevention (DLP) tools to monitor and prevent sensitive information from leaving the system unintentionally.
Compliance with Data Privacy Regulations
Adherence to data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, and others relevant to your organization’s location and operations, is non-negotiable. These regulations mandate specific data handling practices, including consent management, data subject access requests, and data breach notification procedures. The knowledge base must be configured and managed in a way that fully complies with these regulations. This involves careful consideration of data retention policies, ensuring data is only collected and stored for legitimate business purposes, and providing users with transparent control over their personal data.
Regular training for knowledge base administrators and users on data privacy best practices is essential.
Content Integrity and Authenticity
Maintaining the integrity and authenticity of knowledge base content is vital for its reliability and trustworthiness. Version control systems allow for tracking changes, identifying authors, and reverting to previous versions if necessary. Digital signatures or similar technologies can be used to verify the authenticity of documents and prevent tampering. Regular backups of the knowledge base are crucial for disaster recovery and business continuity, ensuring that information can be restored in the event of a system failure or data loss.
These backups should be stored securely, ideally in a geographically separate location.
Preventing Unauthorized Access and Data Breaches
Preventing unauthorized access requires a multi-layered approach. This includes strong password policies, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and regular security awareness training for users. Regularly reviewing and updating user permissions is essential to ensure only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information. Implementing intrusion detection and prevention systems can help detect and respond to malicious activities. Furthermore, establishing clear incident response procedures is crucial for handling security incidents effectively and minimizing the impact of potential data breaches.
Regular penetration testing and security audits help identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by malicious actors.
Measuring Knowledge Base Effectiveness
The true measure of a knowledge base isn’t its size, my friends, but its impact. A sprawling repository of information is useless if it doesn’t empower users and streamline processes. To truly understand the value we’re delivering, we must meticulously track its effectiveness. This involves a careful selection of key performance indicators (KPIs), a robust feedback mechanism, and insightful reporting.
Only then can we refine and optimize this invaluable resource.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Understanding the effectiveness of our knowledge base requires a nuanced approach, going beyond simple metrics. We need to track indicators that directly reflect its impact on user experience and operational efficiency. These KPIs provide a comprehensive picture of our knowledge base’s performance.
- Search Success Rate: The percentage of searches that result in the user finding a relevant and helpful answer. A high success rate indicates effective indexing and organization.
- Average Time to Resolution: The average time it takes a user to find a solution to their problem using the knowledge base. Lower times indicate efficiency and ease of use.
- Knowledge Base Article Views: The total number of times articles within the knowledge base are viewed. This helps identify popular and less-utilized articles, informing content updates and prioritization.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) Score: A direct measure of user satisfaction with the information provided. This is usually collected through post-search or post-article surveys.
- Ticket Deflection Rate: The percentage of support tickets avoided due to users finding solutions within the knowledge base. This demonstrates a significant return on investment.
Collecting User Feedback
Gathering user feedback is the lifeblood of improvement. It’s not just about numbers, but about understanding the user journey and pain points. We need to create opportunities for users to share their experiences, both positive and negative.
We can implement several methods:
- Post-Search/Article Surveys: Simple surveys prompting users to rate their satisfaction and provide comments after using the knowledge base.
- In-App Feedback Forms: Easy-to-access forms within the knowledge base itself, allowing users to provide immediate feedback.
- Focus Groups: Targeted discussions with a smaller group of users to gain in-depth insights into their experiences.
- User Interviews: One-on-one interviews to explore specific aspects of user interaction with the knowledge base.
Example Reports
Data, my friends, is the key to unlocking true understanding. Regular reports provide valuable insights into knowledge base performance and user behavior.
Here are some examples:
- Search Term Report: A report detailing the most frequently searched terms, revealing common user questions and potential gaps in the knowledge base.
- Article Performance Report: A report showing the number of views, average time spent on each article, and user satisfaction scores for each article. This allows us to identify top-performing and underperforming articles.
- Ticket Deflection Report: A report illustrating the number of support tickets avoided thanks to the knowledge base, demonstrating its effectiveness in reducing support workload.
- User Feedback Summary Report: A compilation of user feedback, highlighting common issues, suggestions for improvement, and overall sentiment.
Strategies for Improvement
The analysis of data isn’t an end in itself, but a pathway to continuous improvement. By carefully analyzing the reports and feedback, we can implement targeted strategies to enhance the knowledge base’s effectiveness.
Some examples include:
- Content Updates: Updating existing articles based on user feedback and search data to ensure accuracy and relevance.
- Content Creation: Creating new articles to address identified knowledge gaps and frequently asked questions.
- Improved Search Functionality: Optimizing the search engine to improve search accuracy and relevance.
- Usability Enhancements: Improving the overall user interface and navigation of the knowledge base based on user feedback.
- Training and Communication: Educating users on how to effectively utilize the knowledge base.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Navigating the intricacies of the Microsoft Teams knowledge base can sometimes present unforeseen challenges. This section serves as a guide to address common hurdles, empowering you to swiftly resolve issues and maintain a seamless experience. We’ll explore typical problems, offer detailed solutions, and provide a concise FAQ to address frequently asked questions.
Access Denied Errors
Access denied errors often arise from insufficient permissions. This can manifest as an inability to view, edit, or create knowledge base articles. The resolution involves verifying user roles and permissions within the Teams administration console. Ensure the user belongs to the appropriate group with the necessary access rights. If the issue persists, consult your Teams administrator for assistance in assigning or modifying permissions.
Correctly configured permissions are fundamental to a functional and secure knowledge base.
Search Functionality Issues
Difficulties with the knowledge base search function, such as returning irrelevant results or failing to locate relevant articles, often stem from inadequate indexing or incorrect search queries. To troubleshoot, refine your search terms using s specific to the desired information. If the problem persists, check the indexing status of the knowledge base within the administrative settings. Re-indexing the knowledge base might be necessary to ensure all content is properly searchable.
Consider also the use of advanced search operators (e.g., wildcards, Boolean operators) to enhance search precision.
Content Synchronization Problems
Synchronization issues between the knowledge base and other connected Microsoft services, such as SharePoint or OneDrive, can result in inconsistencies or data loss. These issues typically arise from network connectivity problems or conflicts in data versions. First, verify network connectivity and ensure that all necessary services are running. Then, check for any conflicting versions of documents and resolve these conflicts manually or through the use of version control tools.
Regularly scheduled synchronization checks can help prevent major disruptions.
Knowledge Base Article Editing Conflicts
Simultaneous editing of the same knowledge base article by multiple users can lead to data overwrites and loss of information. Microsoft Teams offers features to manage these conflicts. The system often presents a notification indicating a conflict, allowing users to compare different versions and merge changes manually. Alternatively, implementing a version control system and clearly defined editing protocols can minimize these conflicts.
Clearly defined workflows for content creation and updates are essential for effective collaboration and conflict prevention.
FAQ: Common User Questions
A frequently asked question (FAQ) document provides quick answers to common user queries. Below is an example of such a document, addressing typical user concerns:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| How do I create a new knowledge base article? | Navigate to the knowledge base section in Microsoft Teams and select the “New Article” option. Follow the on-screen instructions to create and save your article. |
| How do I search for specific information within the knowledge base? | Use the search bar located at the top of the knowledge base interface. Enter relevant s to filter and find the required information. |
| What should I do if I encounter an access denied error? | Contact your Teams administrator to verify your user permissions and ensure you have the necessary access rights to the knowledge base. |
| How can I update an existing knowledge base article? | Open the article you want to update and make the necessary changes. Remember to save your changes. |
Best Practices for Knowledge Base Design

Crafting a truly effective knowledge base is an art, my friends. It’s not just about compiling information; it’s about creating a seamless, intuitive experience for your users. Think of it as building a bridge—a bridge that connects your users with the answers they desperately seek. A well-designed knowledge base is the cornerstone of efficient problem-solving and empowered users.
It’s a testament to your commitment to their success.Effective knowledge base design hinges on several key principles. We must consider the user journey, the clarity of information, and the overall aesthetic appeal. A poorly designed knowledge base can lead to frustration, wasted time, and ultimately, a diminished user experience. Let us delve into the intricacies of creating a knowledge base that not only informs but also inspires.
Effective Knowledge Base Layouts and Navigation Structures
The architecture of your knowledge base is paramount. A logical and intuitive structure makes finding information a breeze. Consider using a hierarchical structure, organizing information into categories and subcategories. Think of it as a well-organized library, where each book (article) has its designated shelf (category). Another approach is a -based system, allowing users to search directly for specific terms.
A hybrid approach, combining both hierarchical and -based navigation, often proves to be the most effective. Imagine a user interface that seamlessly blends the familiarity of a categorized library with the precision of a powerful search engine. This ensures that regardless of how a user approaches the knowledge base, they will find what they need.
Using Clear and Concise Language in Knowledge Base Articles
Clarity is king, my friends. Avoid jargon, technical terms, and overly complex sentences. Write as you would speak to a friend—clearly, concisely, and with empathy. Each sentence should serve a purpose, each word chosen with intention. Use simple language, avoiding ambiguity and ensuring that the information is easily digestible.
Imagine a user in a hurry, desperately seeking a solution. Your knowledge base should be their sanctuary, a place where they can find answers quickly and efficiently. Short paragraphs and bullet points can significantly enhance readability.
Creating Visually Appealing and Easy-to-Understand Content
The visual appeal of your knowledge base is as important as its content. Use headings, subheadings, and bullet points to break up large blocks of text. Incorporate whitespace strategically to improve readability. Consider using a consistent design template to create a unified and professional look. Think of it as dressing your knowledge base in a well-tailored suit—it immediately projects professionalism and competence.
A visually appealing knowledge base is more engaging and easier to navigate, making it a pleasure to use.
Use of Multimedia Elements to Enhance Knowledge Base Articles
Multimedia elements can significantly enhance the user experience. Images, videos, and interactive elements can make complex information easier to understand and more engaging. A well-placed image can illustrate a concept more effectively than a thousand words. A short video tutorial can guide a user through a process step-by-step. Imagine the power of combining a concise explanation with a visually rich demonstration.
This multi-sensory approach creates a more memorable and effective learning experience. Consider using screenshots to visually guide users through software processes, or short video clips demonstrating complex procedures.
Knowledge Base Layout Comparison
| Layout Option | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hierarchical | Categorized structure with subcategories. | Easy to navigate, logical organization. | Can become unwieldy with large amounts of content. |
| -Based | Users search for specific terms. | Fast retrieval of information, ideal for large KBs. | Requires robust search functionality. |
| Hybrid | Combines hierarchical and -based approaches. | Best of both worlds, balances ease of navigation with powerful search. | More complex to implement. |
| FAQ Style | Organized by frequently asked questions. | Addresses common issues directly, user-friendly. | May not cover all possible scenarios. |
Advanced Features and Customization
Unlocking the true potential of your Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base involves delving into its advanced features and customization options. This allows you to tailor the knowledge base to perfectly fit your organization’s unique needs and workflow, ensuring maximum efficiency and user satisfaction. Think of it as moving from a sturdy, functional house to a magnificent, personalized palace of information.
Beyond the foundational elements, Microsoft Teams’ Knowledge Base offers a suite of sophisticated tools designed to enhance collaboration, control, and the overall user experience. These features empower you to manage your knowledge base with precision and finesse, ensuring its continued relevance and value to your team.
Version History
Version history provides a detailed audit trail of all changes made to articles within the knowledge base. This is invaluable for tracking edits, identifying the source of errors, and even reverting to previous versions if necessary. Imagine a meticulously kept record book, detailing each and every modification to your articles – a safeguard against accidental deletions or unwanted alterations.
The system records the author, date, and time of each change, allowing for seamless collaboration and conflict resolution. This granular level of control ensures data integrity and allows for a smooth workflow, even in dynamic collaborative environments.
Collaborative Editing
Collaborative editing allows multiple users to work simultaneously on the same article, fostering a dynamic and efficient knowledge creation process. This feature transforms the knowledge base into a truly shared space, facilitating real-time updates and eliminating the bottlenecks of sequential editing. Picture a symphony of minds working in harmony, each contributing their expertise to build a comprehensive and accurate knowledge repository.
The integrated comment features further enhance collaboration, enabling users to discuss changes and provide feedback directly within the document.
Approval Workflows
Approval workflows streamline the publication process by requiring articles to be reviewed and approved before they become publicly accessible. This ensures quality control and consistency across the knowledge base, preventing the dissemination of inaccurate or incomplete information. Think of this as a rigorous quality check, ensuring that only the most accurate and reliable information reaches your users. You can define specific roles and permissions, ensuring that articles are reviewed by the appropriate subject matter experts before being released.
This controlled process maintains a high standard of information accuracy and reliability.
Customizing Appearance and Functionality
Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base offers robust customization options, enabling you to tailor both its visual presentation and operational aspects to align seamlessly with your brand identity and organizational needs. This allows for a cohesive and user-friendly experience.
Custom Templates and Branding
The ability to create custom templates allows for consistent formatting and branding across all knowledge base articles. This enhances the professional image of your organization and ensures a consistent user experience. Imagine a branded template that mirrors your company’s visual identity, incorporating logos, color schemes, and fonts. This level of customization ensures that the knowledge base is not just functional but also reflects the unique personality and style of your organization.
Similarly, you can customize the overall look and feel of the knowledge base to match your company’s branding, creating a cohesive and professional experience for your users.
Integrating with External Systems
Integrating the knowledge base with external systems such as CRM or ticketing platforms allows for a centralized repository of information, improving efficiency and reducing data silos. This interconnectedness streamlines workflows and minimizes the need for users to switch between different applications. Imagine seamless data flow between your knowledge base and other critical systems, enabling quick access to relevant information from a single, unified platform.
This integration minimizes redundancy and promotes a more efficient and informed workflow across your organization. For instance, automatically updating knowledge base articles based on changes in your CRM database ensures that your information is always current and relevant.
Migration to Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base
Embarking on the journey of migrating your existing knowledge base to Microsoft Teams is a significant undertaking, akin to orchestrating a grand symphony. A well-planned migration ensures a seamless transition, minimizing disruption and maximizing the benefits of Teams’ robust features. This detailed guide will illuminate the path, providing the tools and strategies for a successful migration.
Step-by-Step Guide for Migrating from Confluence
The migration process, my friend, is a delicate dance. Each step must be executed with precision and care. This numbered guide will walk you through the process, transforming your Confluence wiki into a vibrant Microsoft Teams knowledge base. Remember, thorough planning is the cornerstone of success.
- Exporting Confluence Content: Begin by exporting your Confluence content in a suitable format, such as HTML or XML. This process typically involves navigating to your Confluence space’s administration settings and selecting the export option. Imagine this as carefully packaging your precious musical instruments before the concert. A visual representation would show a screenshot of the Confluence export options menu, highlighting the relevant buttons and settings.
- Data Cleaning and Transformation: Once exported, meticulously clean and transform the data to align with Microsoft Teams’ formatting requirements. This might involve removing unnecessary formatting, standardizing headings, and resolving broken links. Consider this phase as tuning each instrument, ensuring each note resonates perfectly. A screenshot could depict a comparison of the raw exported data and the cleaned-up version, highlighting the changes.
- Importing into Microsoft Teams: Leverage the Microsoft Teams interface to import the cleaned data. This typically involves creating new channels or tabs within your Teams workspace and uploading the transformed content. Think of this as arranging the instruments on the stage, ready for the performance. A screenshot would display the Microsoft Teams interface, showing the upload or import function for knowledge base articles.
- Content Type Migration: Handle different content types (articles, FAQs, images, videos) with specific care. For instance, images and videos may require separate uploading and linking within the articles. Visualize this as carefully placing each musician in their designated spot on the stage. A screenshot could illustrate how an image is embedded within a Teams knowledge base article.
- Verification and Testing: After importing, thoroughly verify the accuracy and completeness of the migrated content. Test all links, formatting, and functionality to ensure a flawless experience. This is the final rehearsal before the grand performance. A screenshot could show a checklist for verifying the migrated content.
Data Integrity and Accuracy Strategies
Maintaining the purity and accuracy of your data during migration is paramount, as vital as safeguarding a priceless manuscript. Various strategies can ensure the integrity of your knowledge base.
| Strategy | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Review & Correction | High accuracy, thorough verification | Time-consuming, labor-intensive, prone to human error if not done carefully |
| Automated Data Cleaning | Faster than manual review, efficient for large datasets | Potential for errors if the automation script isn’t robust and thoroughly tested; requires specialized technical skills |
| Cross-referencing with Source | Ensures completeness, allows for easy comparison | Requires access to both source and target systems; may be complex for large datasets |
| Version Control (e.g., Git) | Allows for rollback, tracks changes, facilitates collaboration | Requires technical expertise to set up and manage; adds complexity to the process |
Potential Challenges and Solutions
The path to migration is not always smooth; unforeseen challenges may arise. However, with careful planning and proactive strategies, these hurdles can be overcome.
- Challenge 1: Data Loss during Transfer
Solution: Implement a robust backup and recovery strategy before commencing the migration. Utilize Microsoft Teams’ version history features and consider using a third-party migration tool with robust data validation and error handling. Regularly back up your Confluence data before, during, and after the migration.
- Challenge 2: Formatting Inconsistencies
Solution: Develop a clear style guide for the Microsoft Teams knowledge base
-before* the migration. Use a tool that allows for automated formatting conversion from Confluence to the Teams format. Thoroughly test the conversion process on a small sample of data. - Challenge 3: Integration Problems with Existing Systems
Solution: Thoroughly assess the integrations needed
-before* starting the migration. Plan the integration process in detail, and test thoroughly before migrating the entire knowledge base. Document all integrations and their configurations. - Challenge 4: User Access Control Issues
Solution: Carefully map Confluence user permissions to Microsoft Teams permissions
-before* the migration. Test the access control mechanisms thoroughly after the migration. Provide clear instructions to users on accessing the new knowledge base. - Challenge 5: Outdated Information and Broken Links
Solution: Implement a data cleansing process before migration to identify and fix outdated information and broken links. Use a tool that can automatically detect and flag these issues. Establish a process for regularly updating the knowledge base after migration.
Minimizing User Disruption Communication Plan
Communicating effectively with users is essential for a smooth migration, like tuning an orchestra to a perfect harmony. A well-defined communication plan will minimize disruption and ensure a seamless transition.
| Timeline Stage | Activity | Responsible Party | Target Completion Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Migration (Week 1) | Announcement email to all users, outlining the migration plan, timeline, and expected changes. | Communications Team | October 27, 2023 |
| Migration (Week 2) | Knowledge base migration; scheduled downtime communicated in advance. | IT Department | November 3, 2023 |
| Post-Migration (Week 3) | User training sessions, FAQs, and ongoing support channels established. | Training Team | November 10, 2023 |
| Ongoing | Feedback mechanisms implemented (surveys, suggestion box). | Communications Team | Ongoing |
Summary of the Migration Process
Migrating a knowledge base requires meticulous planning, robust data management, and effective communication. Key learnings include the importance of thorough data cleansing, comprehensive testing, and proactive user communication. Future migrations should incorporate automated tools where feasible and prioritize continuous monitoring and improvement. A well-defined rollback strategy is crucial to mitigate potential issues.
Training and Onboarding for Users: Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base
Embarking on a journey with the Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base requires a well-structured training program. This ensures a smooth transition and empowers users to leverage the system’s full potential, leading to increased efficiency and collaboration. A multi-modal approach caters to diverse learning styles, maximizing knowledge retention and user satisfaction.
Multi-Modal Training Program Design
A comprehensive training program incorporates various learning methods to cater to diverse learning preferences. This program is structured in four modules, each designed to build upon the previous one, culminating in a confident and proficient user experience.
- Module 1: Introduction to the Knowledge Base (5-10 minute video tutorial): This introductory module familiarizes users with the knowledge base’s navigation, search functionalities, and key features. A short quiz reinforces learning and assesses comprehension.
- Module 2: Creating and Editing Knowledge Base Articles (15-20 minute interactive tutorial with embedded exercises): This module provides hands-on experience in article creation, focusing on formatting (headings, lists, bold/italic text), image insertion, and version control. Example articles are provided for replication, ensuring practical application of learned skills.
- Module 3: Searching and Utilizing the Knowledge Base Effectively (10-15 minute video tutorial with downloadable cheat sheet): This module delves into advanced search techniques, filtering options, and the effective utilization of the knowledge base’s organizational structure. A downloadable cheat sheet provides a quick reference for future use.
- Module 4: Collaboration and Knowledge Base Maintenance (10 minute video tutorial): This module emphasizes collaboration aspects, covering article co-authoring, updating existing articles, and managing article versions. It promotes a collaborative and efficient workflow.
Comprehensive User Guide
A detailed user guide complements the training program, providing step-by-step instructions and visual aids. This guide mirrors the training modules’ structure, ensuring consistency and easy navigation.
- Section 1: Getting Started: This section includes screenshots of the login screen, the main dashboard, and the primary navigation menus, providing a clear visual path for initial navigation.
- Section 2: Creating Articles: This section offers step-by-step instructions, accompanied by screenshots, detailing article creation, formatting options, and image insertion. Each step is clearly illustrated.
- Section 3: Editing Articles: This section explains the process of editing existing articles, including version history management and collaboration features. Screenshots illustrate the workflow.
- Section 4: Searching and Filtering: This section elucidates advanced search operators and filtering options, enhanced with illustrative screenshots for clarity.
- Section 5: Troubleshooting Common Issues: This section addresses frequently encountered problems and their solutions, offering practical guidance and resolving common user challenges.
The guide will be available in PDF and accessible HTML formats, adhering to WCAG guidelines for broad accessibility.
Examples of Effective Training Materials
A variety of training materials cater to different learning styles. These materials are designed to be engaging, informative, and easily digestible.
| Material Type | Description | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Short Explainer Video | Concise videos demonstrating key features. | A 60-second video demonstrating the creation of a new article, highlighting key steps and features. |
| Interactive Tutorial | Step-by-step guided exercises with immediate feedback. | A tutorial guiding users through creating an article with multiple sections, including image insertion, with immediate feedback on correct actions. |
| Scenario-Based Videos | Demonstrates using the knowledge base in realistic work situations. | A video depicting a user troubleshooting a common issue using the knowledge base’s search and filtering functionalities. |
| Animated GIFs | Short animated sequences illustrating specific actions or workflows. | An animated GIF demonstrating the use of advanced search filters, showing the step-by-step process visually. |
Best Practices for Ongoing User Support and Maintenance
Sustaining a vibrant and effective knowledge base necessitates ongoing support and maintenance. A proactive approach ensures its continued relevance and usability.
- Regular Updates: A scheduled update process ensures the knowledge base reflects the latest changes in Microsoft Teams, maintaining accuracy and relevance.
- Feedback Mechanism: A system for collecting user feedback on both the knowledge base and training materials allows for continuous improvement based on user experience.
- Knowledge Base Governance: Clear guidelines for article creation, editing, and approval ensure consistency, accuracy, and maintain the quality of information.
- User Community Forum: A dedicated forum encourages user interaction, allowing for question-answering and the sharing of best practices, fostering a collaborative environment.
- Metrics Tracking: Key performance indicators (KPIs) track knowledge base usage and effectiveness, providing data-driven insights for continuous improvement.
Cost and Licensing Considerations
Navigating the financial landscape of implementing a Microsoft Teams knowledge base requires a clear understanding of licensing, implementation, and maintenance costs. This section provides a comprehensive overview to help you make informed decisions and optimize your investment. We’ll delve into licensing requirements, implementation and maintenance expenses, cost-effectiveness comparisons against alternatives, and strategies for cost reduction.
Licensing Requirements
Understanding the licensing tiers for Microsoft Teams is crucial for accessing and utilizing the knowledge base feature. Different licenses offer varying levels of access, impacting both cost and functionality. Microsoft 365 licenses that include Microsoft Teams typically provide access to the knowledge base. However, the specific permissions (creation, editing, viewing) depend on the license type assigned to each user.
For instance, a Microsoft 365 E3 license grants full access, while a Microsoft 365 F1 license might only allow viewing. Guest users and external collaborators often have limited editing capabilities, potentially reducing licensing costs but also restricting collaboration. License limitations on the size or number of knowledge base articles are generally not strictly enforced, instead being subject to overall Microsoft 365 tenant storage limits.
Acquiring and managing licenses involves the Microsoft 365 admin center, where licenses can be assigned, modified, and removed as needed through a straightforward user interface.
Implementation and Maintenance Costs
Implementing a Microsoft Teams knowledge base involves both one-time and recurring costs. One-time costs might include consulting fees for initial setup and configuration, although this can often be minimized with internal resources or readily available online guides. Recurring costs are primarily driven by Microsoft 365 licensing fees, storage costs (based on the amount of content and attached files), and potential support fees for escalated issues.
Training employees on knowledge base usage and maintenance is another ongoing expense, potentially requiring internal training sessions or external consulting. Ongoing maintenance involves keeping the knowledge base up-to-date with software updates, security patches, and regular data backups. Data migration from a legacy system, if applicable, would also add to the initial implementation cost. For example, migrating 10,000 articles from a legacy system could take several days of consultant time, adding significantly to the initial outlay.
Cost-Effectiveness Comparison
Comparing the total cost of ownership (TCO) of the Microsoft Teams knowledge base with alternatives is essential for justifying the investment. Let’s consider three alternatives: SharePoint Online, Confluence, and a custom-built solution.
| Feature | Microsoft Teams KB | SharePoint Online | Confluence | Custom-Built Solution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Licensing Costs | Varies with Microsoft 365 license tier | Varies with SharePoint license tier | Subscription based, varies with user count and features | Significant upfront and ongoing development costs |
| Implementation Costs | Low to moderate, depending on existing infrastructure | Moderate, requiring configuration and potential customization | Moderate, involving setup, configuration, and potential integration | High, including design, development, testing, and deployment |
| Maintenance Costs | Low to moderate, included in Microsoft 365 subscription | Moderate, requiring ongoing maintenance and updates | Moderate, involving updates, support, and potential add-on costs | High, including ongoing maintenance, bug fixes, and feature enhancements |
| Scalability | High, scales with Microsoft 365 infrastructure | High, scales with SharePoint infrastructure | High, scales with Confluence infrastructure | Moderate to high, depending on design and architecture |
| Integration | Seamless integration with other Microsoft services | Good integration with other Microsoft services | Integration with other tools may require additional work | Integration depends on design and development choices |
Return on investment (ROI) analysis for each solution should consider factors like improved employee productivity (reduced time spent searching for information), reduced support costs (fewer calls to the help desk), and increased efficiency. A detailed ROI calculation would require specific data on current support costs and projected improvements in productivity.
Cost-Saving Strategies
Several strategies can significantly reduce the overall cost of the Microsoft Teams knowledge base. Firstly, optimizing content creation and management through templates and standardized processes can minimize the time and resources required for content creation and maintenance. Secondly, leveraging existing internal expertise for knowledge base administration and training can reduce reliance on external consultants, lowering both implementation and maintenance costs.
Thirdly, implementing automation tools for tasks like content updates and workflow automation can streamline processes, saving both time and money. Optimizing knowledge base usage involves regular content review and archiving of obsolete information to minimize storage costs. Careful consideration of license assignments, ensuring only necessary users have access to editing permissions, further reduces licensing fees.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Creating a truly impactful knowledge base isn’t just about comprehensive information; it’s about ensuring that information is accessible to everyone, regardless of their abilities. An inclusive knowledge base breaks down barriers and empowers all users to find the answers they need, fostering a more equitable and productive environment. This section delves into the crucial aspects of designing and developing an accessible and inclusive Microsoft Teams knowledge base.Accessibility isn’t just a matter of compliance; it’s a fundamental aspect of good design.
By prioritizing accessibility, we ensure that our knowledge base serves its intended purpose for the widest possible audience. This includes users with visual, auditory, motor, cognitive, and other disabilities. Building an inclusive environment benefits everyone, promoting a more user-friendly and effective resource for all.
Alternative Text for Images
Effective use of alternative text (alt text) is paramount for visually impaired users who rely on screen readers. Alt text provides a textual description of an image, conveying its meaning and context. Instead of simply stating “image of a graph,” a detailed description such as “Bar graph showing the increase in user engagement from January to March, with a peak in February at 75%,” is significantly more informative and helpful.
Consider the image’s purpose and function within the context of the surrounding text when writing alt text. Avoid redundant descriptions; focus on conveying the essential information. For example, if an image is purely decorative, use empty alt text (” “).
Transcripts for Videos
Similarly, providing transcripts for videos makes the information accessible to deaf or hard-of-hearing users, as well as those who prefer to read rather than watch. Accurate and complete transcripts allow everyone to engage with the video content fully. Furthermore, transcripts improve search engine optimization () by providing additional text for indexing, making the video content more discoverable. Consider using automated transcription services and then meticulously reviewing and editing the output to ensure accuracy and clarity.
Tools and Techniques for Ensuring Accessibility
Several tools and techniques can help ensure knowledge base accessibility. Screen readers, such as JAWS and NVDA, can be used to test the accessibility of content. These tools simulate the experience of a visually impaired user, highlighting potential accessibility issues. Automated accessibility checkers, integrated into many content management systems (CMS) or available as browser extensions, can identify potential problems like missing alt text or insufficient color contrast.
These tools provide valuable feedback, helping identify areas for improvement. Regular accessibility audits, performed by experts, can offer a comprehensive assessment and recommendations for enhancing accessibility. Following established accessibility guidelines, such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines), is also crucial. These guidelines provide a framework for creating accessible web content, ensuring compatibility across various assistive technologies.
Future Trends and Developments
The Microsoft Teams knowledge base, already a powerful tool, stands poised for significant advancements. Its future hinges on leveraging emerging technologies and adapting to evolving workplace dynamics. This section explores potential developments, emerging trends, and the future role of the Teams knowledge base in shaping the modern workplace.
Future Enhancements for the Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base
Several key areas within the Microsoft Teams knowledge base are ripe for improvement. These enhancements will significantly boost user experience, efficiency, and overall effectiveness.
Search Functionality Improvements, Microsoft teams knowledge base
Improved search algorithms will be crucial. Semantic search, understanding the meaning and context of queries rather than just s, will dramatically improve accuracy. Fuzzy matching will tolerate minor spelling errors, ensuring users find relevant information even with typos. Faceting options, allowing users to filter results by categories, dates, authors, or other metadata, will refine search results. Personalized search results, tailored to user roles and past activity, will deliver highly relevant information quickly.
For example, a sales representative might see sales-related documents prioritized in their search results, while an IT professional would see technical documentation.
Content Creation and Management Advancements
Collaborative authoring tools will evolve to allow real-time co-editing with integrated commenting and version history. This fosters seamless teamwork and avoids confusion from multiple revisions. Advanced version control systems will provide a detailed audit trail of changes, facilitating accountability and enabling easy rollback to previous versions if needed. Automated content tagging and categorization using AI will ensure consistent organization and efficient retrieval.
Workflows for content approval will ensure quality control and consistency before publishing. For example, a new feature could automatically tag articles based on their content, assigning them to relevant categories and making them easier to find.
Enhanced Integration with Other Microsoft 365 Services
Deeper integration with Power BI will enable dynamic dashboards displaying key knowledge base metrics, such as article views, user engagement, and search trends. This provides valuable insights into knowledge base usage and effectiveness. Power Automate will automate repetitive tasks like content migration, updates, and notifications, freeing up administrators’ time. Integration with SharePoint will offer robust content storage, governance, and compliance capabilities.
For instance, a Power Automate flow could automatically update a knowledge base article whenever a related SharePoint document is modified.
Accessibility and Inclusivity Advancements
Improved screen reader compatibility will ensure that users with visual impairments can easily access and navigate the knowledge base. Automatic alt text generation for images will enhance accessibility for visually impaired users and improve . Support for multiple languages will cater to diverse workforces and global audiences. Features promoting inclusivity will include guidelines for creating diverse and unbiased content, ensuring the knowledge base reflects the organization’s commitment to inclusivity.
For example, the system could suggest alternative phrasing to avoid gendered language or culturally insensitive terms.
Emerging Trends in Knowledge Management
Several emerging trends will significantly impact the future of knowledge management and the Teams knowledge base.
AI-Powered Knowledge Management
AI will play a pivotal role in automating various aspects of knowledge management. AI-powered chatbots will provide instant answers to frequently asked questions, freeing up human support staff. Natural language processing (NLP) will enable intelligent search and content summarization, making information easier to find and understand. For example, an AI-powered chatbot could answer basic questions about company policies, while NLP could summarize lengthy documents into concise summaries.
Microlearning and Personalized Learning Paths
The Teams knowledge base will increasingly support microlearning initiatives, delivering bite-sized learning modules focused on specific skills or topics. AI-driven personalized learning paths will adapt to individual user needs and skill gaps, ensuring users receive relevant training. This approach boosts knowledge retention and improves employee skill development. For example, the system could recommend specific articles or training modules based on a user’s role and performance.
Knowledge Graphs and Semantic Technologies
Knowledge graphs will enhance knowledge discovery and retrieval by representing information as interconnected nodes and relationships. This semantic approach allows for more nuanced and context-aware search, leading to more accurate and relevant results. While implementing knowledge graphs can be complex, the benefits in terms of improved knowledge discovery and understanding outweigh the challenges. For example, a knowledge graph could link related articles, allowing users to explore interconnected concepts and deepen their understanding.
The Metaverse and Immersive Knowledge Sharing
The metaverse offers exciting possibilities for immersive knowledge sharing. Virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) technologies can create interactive training simulations, virtual tours of facilities, or collaborative 3D models for explaining complex processes. However, widespread adoption faces challenges like the cost of VR/AR equipment and the need for user training. For example, a company could use VR to train employees on operating complex machinery in a safe and controlled environment.
Future Role of the Teams Knowledge Base in the Workplace
The Teams knowledge base will play a transformative role in the future workplace.
Evolution of the Workplace
The Teams knowledge base will seamlessly adapt to hybrid and remote work models by providing centralized access to information regardless of location. Its accessibility and collaborative features will support geographically dispersed teams.
Employee Experience
The knowledge base will significantly improve employee onboarding, training, and self-service support. Easy access to information empowers employees to resolve issues independently, reducing reliance on support staff. Personalized learning paths enhance skill development and boost employee engagement.
Business Value
A robust knowledge base will demonstrably improve key business metrics. Studies show that efficient knowledge sharing can boost employee productivity by 25-30% by reducing time spent searching for information. Improved self-service support can decrease customer support costs by 15-20%. These improvements translate to a significant return on investment.
Competitive Advantage
Organizations with a well-structured and easily accessible knowledge base gain a competitive advantage by fostering a culture of learning, empowering employees, and improving operational efficiency. This attracts and retains top talent while streamlining processes.
Evolution of the Teams Knowledge Base to Meet Changing Organizational Needs
| Organizational Need | Predicted Evolution of Teams Knowledge Base | Specific Example |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Data Security | Enhanced encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention features. | Implementation of zero-trust security model, with granular access control based on user roles and data sensitivity. |
| Improved Collaboration | Integration with advanced collaboration tools and enhanced version control. | Real-time co-authoring with integrated commenting and version history tracking, allowing for seamless collaboration and transparent change management. |
| Enhanced Scalability | Ability to handle exponentially increasing amounts of data and users. | Scalable cloud-based architecture and distributed search indexing to handle massive data volumes and ensure fast search performance even with a large user base. |
| Greater Personalization | AI-driven personalized recommendations and learning paths. | Adaptive learning modules that adjust based on user performance, providing targeted content and support tailored to individual skill gaps and learning styles. |
SWOT Analysis of the Future Potential of the Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base
Strengths: Integration with existing Microsoft ecosystem, large user base, robust security features, flexible deployment options.
Weaknesses: Potential for information silos if not properly managed, complexity of implementation for large organizations, reliance on user participation for content creation.
Opportunities: Integration with emerging technologies like AI and VR, expansion into new markets (e.g., education, healthcare), development of advanced analytics capabilities.
Threats: Competition from other knowledge management platforms, evolving user expectations, the need for continuous updates and improvements to remain relevant.
Question Bank
What are the storage limits for articles in the Microsoft Teams Knowledge Base?
Storage limits depend on your Microsoft 365 plan and overall tenant storage. There are also limits on individual file sizes within articles.
Can I embed external links within my knowledge base articles?
Yes, you can embed links to external websites and resources within your articles.
How do I track the usage and effectiveness of my knowledge base?
Microsoft Teams provides analytics on article views and searches. You can also integrate with Power BI for more in-depth analysis.
What happens if two users edit the same article simultaneously?
Microsoft Teams handles concurrent edits, usually by prioritizing the last saved version. Version history allows reverting to previous versions if needed.
Can I customize the look and feel of my knowledge base?
While extensive customization is limited, you can control branding elements and article formatting to some degree.


