Genesys Knowledge Base represents a pivotal tool for modern customer service, seamlessly integrating information management with customer interaction. Its core functionality extends beyond simple article storage; it’s a dynamic system designed for efficient knowledge creation, organization, and retrieval, ultimately enhancing both agent performance and customer satisfaction. Understanding its capabilities is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their support strategies and improve operational efficiency.
This exploration delves into the Genesys Knowledge Base’s architecture, examining its integration with Genesys Cloud, content management features, sophisticated search algorithms, user experience considerations, security protocols, and future trends. We’ll uncover best practices for maximizing its potential and address common challenges faced by administrators and end-users alike. The goal is to provide a comprehensive guide for anyone seeking to leverage this powerful tool to its fullest extent.
Genesys Knowledge Base Overview
The Genesys Knowledge Base is a centralized repository of information designed to empower contact center agents and improve customer service experiences. It serves as a single source of truth for resolving customer issues quickly and efficiently, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. The system’s effectiveness hinges on its accessibility, searchability, and the quality of the information it contains.The core functionalities of the Genesys Knowledge Base center around providing agents with immediate access to relevant information.
This includes robust search capabilities, allowing agents to quickly find answers to customer queries. The system typically offers features such as article management, version control, and analytics to track knowledge base usage and effectiveness. Integration with other Genesys applications, such as Genesys Cloud, allows for seamless access within the agent’s workflow.
Types of Content within a Genesys Knowledge Base
A Genesys Knowledge Base typically houses a diverse range of content types to address various customer needs and agent queries. This variety ensures comprehensive support and efficient problem resolution. The specific content will vary depending on the business and its products or services.
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): These concise answers address common customer inquiries, providing quick resolutions to simple problems.
- Troubleshooting Guides: Step-by-step instructions for resolving technical issues or common product problems.
- Product Information: Detailed descriptions of products or services, including features, specifications, and usage instructions.
- Process Documents: Internal procedures and guidelines for agents to follow when handling specific situations or customer requests.
- Policy Documents: Information on company policies relevant to customer interactions, such as return policies or privacy policies.
Business Applications of the Genesys Knowledge Base
Businesses leverage the Genesys Knowledge Base in numerous ways to optimize customer support and improve operational efficiency. Effective implementation leads to tangible improvements across various metrics.
- Reduced Average Handling Time (AHT): By providing agents with quick access to information, the Knowledge Base significantly reduces the time spent resolving customer issues.
- Improved First Contact Resolution (FCR): Agents can resolve customer issues on the first contact, leading to increased customer satisfaction and reduced call volume.
- Enhanced Agent Performance: The Knowledge Base empowers agents with the information they need to confidently handle customer inquiries, improving their performance and reducing stress.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Faster resolution times and accurate information contribute to a positive customer experience, boosting satisfaction levels.
- Consistent Messaging: The Knowledge Base ensures all agents deliver consistent and accurate information to customers, strengthening brand reputation.
For example, a telecommunications company might use its Genesys Knowledge Base to provide agents with detailed troubleshooting guides for common internet connectivity problems, while a retail company might use it to house information on return policies and product specifications. A financial institution might utilize it to provide agents with up-to-date information on account management procedures and security protocols. In each case, the Knowledge Base plays a crucial role in streamlining operations and improving the customer experience.
Integration with Genesys Cloud
The Genesys Knowledge Base seamlessly integrates with Genesys Cloud, providing a unified platform for managing and accessing knowledge articles directly within the agent desktop. This integration streamlines workflows, enhances agent efficiency, and ultimately improves the customer experience. The intuitive design ensures a smooth transition for agents already familiar with the Genesys Cloud environment.The integration enhances customer service efficiency by reducing average handling time (AHT), improving first call resolution (FCR), and empowering agents with readily available information to address customer inquiries accurately and promptly.
This leads to increased customer satisfaction and reduced operational costs associated with longer call durations and repeated interactions.
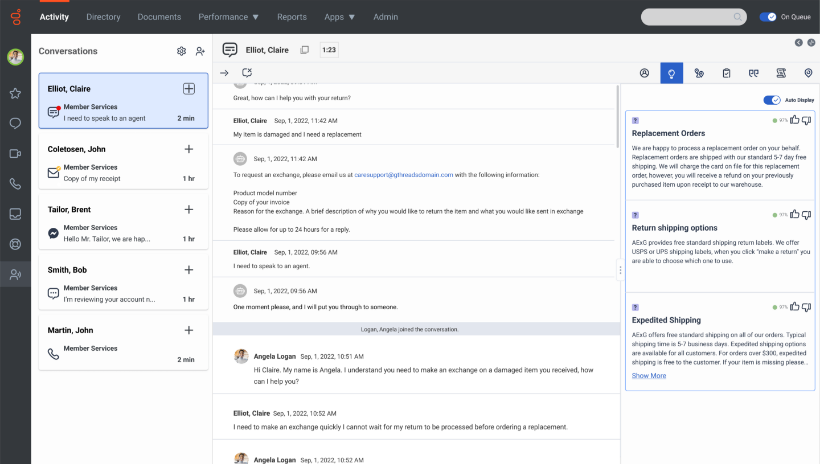
Agent Access and Utilization of Knowledge Base Articles
Agents access knowledge base articles during customer interactions through various methods depending on the configuration. Common methods include embedded search bars within the Genesys Cloud interface, direct links to relevant articles based on the interaction’s context (e.g., through routing or recognition), and proactive suggestions of relevant articles during the call. Agents can then easily view and share the content with the customer, either by reading it aloud or displaying it on a screen share.
This ensures that agents always have the most up-to-date and accurate information at their fingertips, leading to improved responses and resolutions.
Configuring Genesys Knowledge Base Integration with Genesys Cloud
Configuring the integration involves a series of steps that typically require administrative access within both the Genesys Knowledge Base and Genesys Cloud platforms. The specific steps may vary slightly depending on the versions of the software being used, but generally follow this pattern.
- Authentication and Authorization: Establish a secure connection between the Genesys Knowledge Base and Genesys Cloud by configuring appropriate authentication credentials. This often involves generating API keys and access tokens within both systems and securely storing them.
- Data Mapping and Synchronization: Map the relevant data fields between the two systems to ensure seamless data transfer. This may include mapping categories, tags, and other metadata to facilitate efficient searching and retrieval of knowledge articles within Genesys Cloud.
- Integration Configuration within Genesys Cloud: Configure the Genesys Cloud application to connect with and utilize the Genesys Knowledge Base. This typically involves specifying the endpoint URL and authentication details of the Knowledge Base.
- Testing and Validation: Thoroughly test the integration to ensure all features are functioning correctly. This includes testing search functionality, article retrieval, and the overall agent experience within the Genesys Cloud environment.
- Deployment and Monitoring: Deploy the integration to the production environment and continuously monitor its performance. This ensures ongoing stability and identifies any potential issues promptly.
Search and Retrieval Functionality
The Genesys Knowledge Base employs a robust search and retrieval system designed to efficiently locate relevant information within its extensive collection of articles and resources. This system leverages advanced search algorithms and a user-friendly interface to ensure a positive user experience and quick access to needed information. The following sections detail the functionality, algorithms, and strategies employed to optimize search accuracy and relevance.
Search Options within the Genesys Knowledge Base
The Genesys Knowledge Base offers a variety of search options to facilitate efficient information retrieval. Users can employ various search operators and specify search fields to refine their results.
The supported search operators include Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), wildcards (*), and phrase searching (” “). For example, searching for “customer AND support” will return only articles containing both terms. Using “customer OR service” will return articles containing either term. “customer NOT billing” excludes articles mentioning billing. A wildcard search such as “custom*” will return articles containing words starting with “custom,” like “customer” or “customization.” Phrase searching, using quotation marks, ensures the exact phrase is found, as in searching for `”account activation”`.
Searches can be targeted to specific fields, including title, content, tags, and author. Searching within the title field, for example, using “title:account activation”, will only return articles with “account activation” in the title. Similarly, searching within the content field will only return articles where the appears in the body text.
Advanced search options, such as filtering by date, language, or article type, further refine search results. For instance, users can specify a date range to find articles published within a particular timeframe. Language filtering allows users to restrict results to articles in a specific language. Article type filtering can be used to find only FAQs, how-to guides, or other specified document types.
The user interface features a prominently placed search bar, typically at the top of the page. As the user types, autocomplete suggestions appear, assisting in the selection of relevant s or phrases. Search results are displayed in a clear, organized format, often including article titles, snippets of content, and metadata such as author and publication date.
Search Algorithm and its Impact on Knowledge Retrieval
The Genesys Knowledge Base utilizes a sophisticated search algorithm, likely a variant of BM25 (Best Match 25), a probabilistic retrieval model known for its effectiveness in ranking documents based on relevance. BM25 is chosen for its ability to handle large datasets efficiently and accurately, a critical requirement for a knowledge base of significant size.
The algorithm incorporates techniques for handling synonyms, stemming, and lemmatization to improve search accuracy. Synonyms are considered to broaden search scope, while stemming (reducing words to their root form) and lemmatization (reducing words to their dictionary form) help match variations of the same word. For instance, searching for “activate” might also return results containing “activation” or “activated”.
Search result ranking is determined by a relevance score, considering factors such as the frequency of s within the article, the location of s (title vs. body text), and the overall quality and relevance of the article’s content. Higher scores indicate greater relevance.
While the BM25 algorithm is highly effective, limitations exist. For instance, handling complex queries with multiple, nuanced relationships between s might not always yield perfectly accurate results. The impact of these limitations is difficult to quantify precisely but could manifest as a small percentage of irrelevant results returned in some search instances.
Strategies for Improving Search Accuracy and Relevance
Several strategies can be employed to further enhance the accuracy and relevance of search results. Improving metadata tagging through the use of consistent and comprehensive sets is crucial. Best practices include utilizing a controlled vocabulary and hierarchical tagging structures to ensure clarity and consistency across all articles.
Improving the quality of knowledge base content directly impacts searchability. Employing consistent terminology throughout all articles and maintaining clear, concise writing style significantly improves the algorithm’s ability to accurately match user queries with relevant articles. Regular reviews and updates of existing articles also ensure the information remains accurate and current.
User feedback is invaluable for improving search relevance. A feedback mechanism, such as a “thumbs up/thumbs down” rating system or a short feedback form after each search, can be implemented. This data can be analyzed to identify areas where the search algorithm or content needs improvement. For example, consistently low ratings for certain search terms can indicate a need for improved tagging or content revision.
A/B testing can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of different search algorithm parameters or UI elements. For example, different ranking algorithms or autocomplete suggestion mechanisms can be tested to determine which provides the best user experience and most accurate results. This iterative approach allows for continuous optimization of the search system.
User Experience and Accessibility
A user-friendly and accessible Genesys Knowledge Base is crucial for maximizing agent efficiency and ensuring high customer satisfaction. A well-designed knowledge base empowers agents to quickly resolve customer issues, leading to reduced handling times and improved first-contact resolution rates. Conversely, a poorly designed system frustrates agents, increasing their workload and negatively impacting customer experience. This section details the key elements of a successful, accessible knowledge base design.
User-Friendly Interface for Genesys Knowledge Base
A user-friendly interface is paramount for a successful Genesys Knowledge Base. Intuitive navigation and readily accessible information directly contribute to increased agent efficiency and improved customer satisfaction. Studies have shown that a well-designed knowledge base can reduce average handling time (AHT) by 15-20% and increase customer satisfaction scores (CSAT) by 10-15%. Poorly designed interfaces, characterized by cluttered layouts, confusing navigation, and difficult search functionality, often lead to agent frustration and prolonged resolution times.
For example, a knowledge base with inconsistent terminology or a poorly structured hierarchy forces agents to spend excessive time searching for relevant information, directly impacting AHT and CSAT. Conversely, a well-organized system with clear navigation and a robust search function allows agents to find solutions quickly, improving both efficiency and customer experience.
Features Enhancing User Experience
Several features significantly enhance the user experience within the Genesys Knowledge Base. Intuitive navigation is key; this includes breadcrumb trails clearly showing the user’s location within the knowledge base, comprehensive sitemaps providing a structured overview of content, and a robust search function with auto-suggestions and filtering options to refine results. Clear article formatting is equally vital. This involves consistent use of headings (H1-H6) to structure information logically, bullet points and numbered lists to organize key information, and visual aids such as images, diagrams, and videos to enhance understanding.
For example, using H1 for main topic, H2 for s, and H3 for supporting details creates a clear hierarchical structure. Effective use of bullet points summarizes key features or steps in a process, while diagrams can clarify complex concepts. Ineffective use might include using excessive headings, inconsistent formatting, or irrelevant visual aids that distract from the core information.
Accessibility Considerations for Users with Disabilities
Accessibility is paramount. Adhering to WCAG 2.1 AA guidelines ensures the Genesys Knowledge Base is usable by individuals with a wide range of disabilities.
| WCAG Guideline | Specific Implementation for Genesys Knowledge Base | Example | Testing Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perceivable (1.1.1) | Ensure all text content has sufficient color contrast. Use a minimum contrast ratio of 4.5:1 for normal text and 3:1 for large text. | Use a color contrast checker tool (e.g., WebAIM) to verify contrast ratios for all text against its background. | Automated testing tools (e.g., WAVE), manual review. |
| Perceivable (1.4.11) | Provide captions and transcripts for all videos. | Use automated captioning tools and manually review/edit for accuracy and completeness. | Manual review, automated captioning software. |
| Operable (2.1.1) | Keyboard navigation must be fully functional throughout the knowledge base. All interactive elements must be accessible via keyboard. | Test all interactive elements (buttons, links, forms) using only the keyboard. | Manual testing. |
| Understandable (3.3.1) | Ensure all content is written in clear, concise language. Use simple sentence structures and avoid jargon. | Use a readability testing tool (e.g., Hemingway Editor) to assess text complexity. Aim for a readability score appropriate for the target audience. | Automated readability tools, manual review. |
Best Practices for Accessible Knowledge Base Design
Implementing best practices ensures accessibility. This includes providing alternative text for all images (describing the image’s content and purpose), implementing keyboard navigation shortcuts for common actions, ensuring compatibility with screen readers, and supporting assistive technologies. For example, semantic HTML using appropriate heading tags (
–) structures the content logically, making it easier for screen readers to interpret. ARIA attributes can enhance accessibility for interactive elements. For instance, `` provides a clear label for screen reader users.User Testing and Feedback
User Testing and Feedback
A comprehensive user testing plan is essential. This plan should include usability testing with agents and customers representing the target audience. A/B testing can compare different interface designs to identify the most effective options. Metrics for success will include task completion rates, time on task, error rates, and user satisfaction scores. Feedback will be collected through surveys, interviews, and observation during testing sessions.
A sample user feedback form might include questions about ease of navigation, clarity of information, and overall satisfaction with the knowledge base.
Documentation and Training
Detailed documentation on accessibility features is crucial, along with training for content creators on accessibility best practices. A style guide will provide clear guidelines on creating accessible content, including instructions on using alternative text, writing clear and concise language, and formatting content appropriately. This style guide should align with WCAG 2.1 AA guidelines and provide specific examples and best practices for the Genesys Knowledge Base platform.
Reporting and Analytics
The Genesys Knowledge Base offers robust reporting and analytics capabilities, providing valuable insights into knowledge base usage, effectiveness, and areas for improvement. These analytics empower administrators to optimize the knowledge base, ensuring it consistently meets the needs of agents and customers. Data-driven decision-making based on these reports leads to a more efficient and effective support system.The Genesys Knowledge Base provides a comprehensive suite of reports designed to track key performance indicators (KPIs) related to knowledge base usage and effectiveness.
These reports offer a detailed view of how the knowledge base is performing, enabling proactive improvements. This data-driven approach allows for continuous optimization and ensures the knowledge base remains a valuable asset for the organization.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
The following KPIs are crucial for monitoring the health and effectiveness of the Genesys Knowledge Base. Tracking these metrics allows for identification of trends and areas requiring attention. Regular review of these KPIs enables data-informed decisions to improve knowledge base performance and user experience.
| KPI | Description | Data Source | Actionable Insights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Article Views | Total number of times articles were viewed. | Genesys Knowledge Base Analytics Dashboard | Identifies popular and underutilized articles, informing content updates and prioritization. |
| Search Success Rate | Percentage of searches resulting in a relevant article being found. | Genesys Knowledge Base Analytics Dashboard | Highlights areas for improvement in search functionality or content organization. Low success rates may indicate a need for improved indexing or optimization. |
| Average Resolution Time | Average time taken to resolve an issue using the knowledge base. | Genesys Cloud Integration Data | Indicates the efficiency of the knowledge base in assisting agents. High average resolution times may suggest a need for improved article clarity or more comprehensive content. |
| Agent Satisfaction | Agent feedback on the usefulness and ease of use of the knowledge base. | Surveys and Feedback Mechanisms | Directly reflects the effectiveness of the knowledge base from the perspective of those who use it most. Low satisfaction scores may indicate areas for improvement in content, navigation, or search functionality. |
Sample Report: Knowledge Base Performance Overview
This sample report illustrates how the KPIs can be presented to provide a concise overview of knowledge base performance. The data presented is illustrative and would be dynamically populated from the Genesys Knowledge Base analytics dashboard.
| Metric | Value | Trend (Last Month) | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Article Views | 15,000 | +10% | Positive |
| Search Success Rate | 85% | -5% | Needs Attention |
| Average Resolution Time | 3 minutes | +1 minute | Needs Attention |
| Agent Satisfaction Score | 4.2/5 | -0.1 | Needs Attention |
Security and Compliance
Genesys Knowledge Base prioritizes the security and compliance of its data and systems, employing robust measures to protect sensitive information and ensure adherence to relevant regulations. This section details the specific security and compliance practices implemented within the Genesys Knowledge Base.
Data Encryption
The Genesys Knowledge Base utilizes AES-256 encryption for data at rest, safeguarding stored information from unauthorized access. Data in transit is protected using TLS 1.2 or higher, ensuring secure communication between clients and the Knowledge Base servers. Key management follows industry best practices, employing a hierarchical key management system with regular key rotation and secure storage of encryption keys.
These keys are managed using a hardware security module (HSM) for enhanced protection.
Access Control
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is implemented to regulate user access to the Genesys Knowledge Base. Access is granted based on predefined roles, limiting users to only the functionalities and data necessary for their tasks.
| Role | Read Permission | Write Permission | Edit Permission | Delete Permission | Other Permissions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Administrator | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Full Control |
| Editor | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Limited Control (e.g., approval workflow for article publishing) |
| Viewer | Yes | No | No | No | None |
| Guest | Yes (Limited) | No | No | No | Access restricted to specified articles only, potentially with time limits. |
Compliance Regulations
The Genesys Knowledge Base is designed to comply with relevant regulations, including GDPR, CCPA, and SOC 2. For GDPR compliance, data processing activities are documented, and user consent is obtained and managed according to the regulation’s requirements. CCPA compliance is ensured through transparent data collection practices and providing users with data access and deletion rights. SOC 2 compliance is maintained through regular audits and adherence to the trust principles of security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
Detailed compliance documentation is maintained and available upon request.
Vulnerability Management
A comprehensive vulnerability management program is in place, encompassing regular penetration testing and vulnerability scanning using industry-standard tools. A dedicated security team actively monitors for vulnerabilities and promptly addresses identified risks. Incident response procedures are well-defined, including steps for containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident analysis. This process involves regular security assessments and penetration testing performed by independent third-party security firms.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Data loss prevention is achieved through a multi-layered approach including regular automated data backups, version control, and robust disaster recovery plans. Backups are performed daily, with a retention policy of at least 90 days. Version control ensures the ability to revert to previous versions of articles in case of accidental modification or data corruption. The disaster recovery plan includes redundant infrastructure and geographically diverse data centers.
User Authentication
The Genesys Knowledge Base supports multi-factor authentication (MFA) and single sign-on (SSO) for enhanced security. MFA is mandatory for all users with administrative privileges, while SSO is integrated with existing enterprise identity providers to streamline user access. The specific authentication requirements vary based on user roles, with higher privilege roles requiring stronger authentication methods.
Security Monitoring and Auditing
Real-time security monitoring tools continuously analyze system activity for suspicious behavior. Detailed audit logs track user activity, including login attempts, access to articles, and any modifications made. These logs are securely stored, with access restricted to authorized personnel only. Retention policies for audit logs adhere to regulatory requirements and internal security policies. Logs are encrypted both at rest and in transit.
Best Practices for Data Privacy
Data privacy is a core principle. The Genesys Knowledge Base adheres to data minimization, purpose limitation, and data anonymization where appropriate. User consent is explicitly obtained and managed through a transparent consent management system, allowing users to control their data and preferences. Data is only processed for specified, explicit, and legitimate purposes.
Incident Response Plan
The incident response plan Artikels the steps to be taken in case of a security breach or data incident. The plan consists of the following phases:
1. Preparation
Establish communication channels and response teams.
2. Detection & Analysis
Identify the incident and its scope.
3. Containment
Isolate affected systems to prevent further damage.
4. Eradication
Remove the threat and restore system integrity.
5. Recovery
Restore data and services.
6. Post-Incident Activity
Conduct a thorough review and implement preventive measures.
7. Reporting
Notify relevant stakeholders and regulatory bodies as required.
Knowledge Base Scalability and Performance
The Genesys Knowledge Base is designed for scalability and high performance, ensuring efficient operation even with substantial growth in content volume and user traffic. Effective strategies are crucial for maintaining optimal response times and a positive user experience as the knowledge base expands. This section details the key aspects of scalability and performance optimization within the Genesys Knowledge Base.Genesys Knowledge Base scalability relies on a robust architecture capable of handling increasing amounts of data and concurrent user requests.
The system utilizes a distributed architecture and employs techniques like load balancing and caching to distribute the workload efficiently across multiple servers. This ensures that the system can handle spikes in traffic and maintain acceptable response times, even during peak usage periods. Furthermore, the database structure is optimized for efficient data retrieval, minimizing query execution times. The platform’s ability to scale horizontally, by adding more servers as needed, allows for seamless adaptation to growing content and user demands without impacting performance.
Scalability Strategies
The Genesys Knowledge Base employs several strategies to ensure scalability. These include horizontal scaling through the addition of servers to handle increased load, vertical scaling by upgrading server hardware for improved processing power and memory, and database optimization techniques such as indexing and query optimization. Regular performance testing and capacity planning are also integral parts of maintaining scalability.
For example, a company experiencing rapid growth in customer support interactions might initially deploy a smaller instance of the knowledge base, and then scale horizontally by adding more servers as the number of articles and users increases. This phased approach ensures efficient resource utilization and avoids unnecessary upfront investment.
Performance Optimization Techniques
Optimizing knowledge base performance centers on minimizing loading times and ensuring efficient search functionality. Strategies include employing caching mechanisms to store frequently accessed data in memory for faster retrieval, optimizing database queries to reduce execution times, and compressing content to reduce bandwidth consumption. Content delivery networks (CDNs) can also distribute content geographically, reducing latency for users in different regions.
For instance, implementing a CDN would significantly improve loading times for users located far from the primary knowledge base server. Regular monitoring and analysis of system logs can identify areas for improvement.
Potential Bottlenecks and Solutions
Potential performance bottlenecks can include database queries that take excessive time to execute, inefficient content delivery, insufficient server resources, and poorly optimized search algorithms. Solutions include optimizing database queries, implementing caching mechanisms, upgrading server hardware, employing load balancing, and refining search algorithms. For example, if a slow database query is identified as a bottleneck, the solution might involve adding indexes to relevant database tables or rewriting the query for improved efficiency.
Similarly, if server resources are insufficient, scaling horizontally or vertically can address the issue.
Knowledge Base Performance Monitoring Checklist
Regular monitoring is crucial for maintaining optimal performance. A comprehensive checklist should include:
- Daily monitoring of server resource utilization (CPU, memory, disk I/O).
- Regular performance testing under simulated peak load conditions.
- Analysis of database query performance and optimization of slow queries.
- Monitoring of knowledge base loading times and search response times.
- Regular review of system logs to identify errors and performance issues.
- Proactive capacity planning to anticipate future growth and resource needs.
This proactive approach ensures early identification and resolution of performance issues, maintaining a responsive and efficient knowledge base for users.
Training and Support Resources
Genesys Knowledge Base offers comprehensive training and support resources to ensure administrators and end-users can effectively utilize its features. These resources are designed to cater to varying levels of expertise and provide assistance across all aspects of the Knowledge Base, from initial configuration to ongoing maintenance and troubleshooting. Access to these resources is crucial for maximizing the platform’s potential and ensuring a seamless user experience.
The following sections detail the available training materials, support channels, and frequently asked questions to facilitate a smooth onboarding and ongoing support experience.
Administrator Training Materials
Administrator training materials provide a thorough understanding of Genesys Knowledge Base administration. These resources cover configuration, permissions management, content moderation, reporting, and advanced features. Training is delivered through various formats to cater to different learning styles and preferences.
- Video Tutorials: Step-by-step video guides covering key administrative tasks. Estimated time commitment: 2-3 hours.
- Online Courses: Interactive online courses with quizzes and assessments to reinforce learning. Estimated time commitment: 4-6 hours.
- PDF Guides: Comprehensive PDF documents providing detailed instructions and best practices. Estimated time commitment: 3-4 hours.
- Live Webinars: Interactive sessions with Genesys experts allowing for Q&A. Estimated time commitment: 1-2 hours.
End-User Training Materials
End-user training focuses on effectively using the Genesys Knowledge Base to find information. These materials cover search functionality, article navigation, feedback mechanisms, and other relevant user features. Training is provided in multiple formats to maximize accessibility and engagement.
- Interactive Tutorials: Engaging tutorials guiding users through the Knowledge Base’s key features. Estimated time commitment: 30 minutes.
- Quick Start Guides: Concise guides providing a rapid overview of the Knowledge Base’s core functionalities. Estimated time commitment: 15 minutes.
- Video Demonstrations: Short videos showcasing how to perform common tasks within the Knowledge Base. Estimated time commitment: 1 hour.
Genesys Documentation and Support Resources Overview
Genesys provides a range of documentation and support resources tailored to different user roles and needs. These resources are regularly updated to reflect the latest features and best practices.
| Resource Category | Content Description | Target Audience | Format Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Administrator Guides | Detailed steps for configuring, managing, and troubleshooting the Knowledge Base. | Administrators | PDF, Video Tutorials, Wiki |
| End-User Guides | Instructions on effectively using the Knowledge Base to find information. | End-Users | PDF, Interactive Tutorials |
| API Documentation | Comprehensive reference for developers integrating with the Knowledge Base. | Developers | API Reference, Code Samples |
| Troubleshooting Documentation | Solutions to common issues and error messages encountered in the Knowledge Base. | Administrators & Users | FAQ, Knowledge Base Articles |
| Release Notes | Details on new features, bug fixes, and updates to the Knowledge Base. | Administrators | Release Notes Document |
Process for Seeking Assistance from Genesys Support Teams
To contact Genesys support, users should first identify the appropriate channel (phone, email, or online portal). Before contacting support, users should gather relevant information, such as error messages, screenshots, and system details. Issues should be described clearly and concisely. Expected response times and escalation procedures are Artikeld in the support documentation. All support interactions should be documented for future reference.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Genesys Knowledge Base
The following addresses common questions regarding the Genesys Knowledge Base.
- Different user roles and permissions: The Genesys Knowledge Base offers various user roles with defined permissions, controlling access to features and functionalities.
- Creating and publishing knowledge base articles: The process involves drafting, reviewing, and publishing articles through the administrative interface.
- Searching for specific information: The Knowledge Base utilizes a robust search engine allowing users to find relevant information quickly and efficiently.
- Providing feedback on articles: Users can submit feedback through designated mechanisms, allowing for continuous improvement.
- Best practices for creating effective articles: Guidelines are provided for creating clear, concise, and easily searchable articles.
- Tracking Knowledge Base performance: Reporting and analytics tools provide insights into usage patterns and effectiveness.
- Security measures: Robust security measures protect the Knowledge Base and its data.
- Integration with other Genesys applications: The Knowledge Base can be integrated with other Genesys applications to enhance workflow efficiency.
- System requirements: Minimum system requirements for accessing and using the Knowledge Base are specified in the documentation.
- Managing user access and permissions: Administrators can manage user access and permissions through the administrative console.
Best Practices for Knowledge Base Design: Genesys Knowledge Base
Effective knowledge base design is crucial for providing users with a seamless and efficient information retrieval experience. A well-structured and easily navigable knowledge base reduces support tickets, improves customer satisfaction, and boosts overall operational efficiency. This section details best practices for design, feedback incorporation, success measurement, and content strategy.
Information Architecture
Effective information architecture is fundamental to a successful knowledge base. This involves carefully considering categorization, tagging, and navigation to ensure users can easily find the information they need. A hierarchical structure, often represented as a tree, organizes information into categories and subcategories. A faceted structure allows users to filter information based on multiple attributes, while a tag-based structure uses s to link related articles.
The optimal structure depends on the content and user needs.
| Knowledge Base Structure | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hierarchical | Organizes information in a tree-like structure with categories and subcategories. | Simple to understand and navigate; easy to implement. | Can become rigid and difficult to adapt to evolving content; may not support complex searches. |
| Faceted | Allows users to filter information based on multiple attributes (facets). | Highly flexible and allows for complex searches; suitable for large and diverse content. | Can be complex to implement and navigate; requires careful planning and design. |
| Tag-based | Uses s (tags) to link related articles. | Highly flexible and adaptable; allows for organic growth of content. | Can be difficult to manage and maintain consistency; may lead to information redundancy. |
Content Structure and Search Functionality
Clear headings, concise language, and consistent formatting are essential for readability and comprehension. Employing consistent formatting throughout the knowledge base ensures a uniform user experience. Search functionality should be optimized for relevant s, incorporate synonyms to broaden search results, and utilize auto-suggestions to guide users towards relevant articles.
User Feedback and Analysis
User feedback is vital for continuous improvement. Methods for collecting feedback include surveys, in-app feedback forms, and analytics tracking of search queries and article views. Analyzing this data allows for identifying areas for improvement in content, navigation, and search functionality. For example, frequently searched terms not yielding relevant results indicate a need for content additions or improved optimization.
Low article satisfaction ratings point to issues with content clarity or accuracy.
Measuring Knowledge Base Success
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are crucial for evaluating knowledge base effectiveness. These metrics provide insights into user engagement and the overall impact of the knowledge base.
| KPI | Description | Tracking Method | Contribution to Success |
|---|---|---|---|
| Search Success Rate | Percentage of searches resulting in a relevant article. | Analytics tracking of search queries and article clicks. | Indicates the effectiveness of search functionality and content organization. |
| Article Satisfaction Ratings | Average rating given by users after viewing an article. | In-app feedback forms or post-article surveys. | Measures content quality, clarity, and relevance. |
| First Contact Resolution Rate | Percentage of user issues resolved through the knowledge base without needing further support. | Integration with support ticketing system. | Indicates the knowledge base’s effectiveness in self-service support. |
| Knowledge Base Usage Statistics | Total number of searches, articles viewed, and time spent on the knowledge base. | Analytics tracking. | Provides insights into overall user engagement and knowledge base adoption. |
Examples of Well-Designed Knowledge Bases
Example 1: Technical Knowledge Base for Software Engineers
Strengths
Detailed technical explanations, comprehensive search functionality with advanced filtering options, robust tagging system allowing for precise searches based on technical terms and code examples, version control for documentation.
Weaknesses
Steep learning curve for new users due to technical depth, potentially overwhelming amount of information for less experienced engineers, infrequent updates to reflect changes in the software.
Example 2: Customer Support Knowledge Base for End-Users
Strengths
Clear and concise language using plain English, intuitive navigation with clear categorization and visual cues, helpful FAQs addressing common issues, use of multimedia like videos and images for better understanding.
Weaknesses
Limited search functionality, potentially lacking in depth for complex issues, infrequent updates leading to outdated information, lack of personalization based on user history or product usage.
Example 3: Internal Knowledge Base for Employees
Strengths
Easy access to internal documents and resources through single sign-on, efficient search functionality integrated with internal systems like directories and project management tools, centralized repository for all internal documentation.
Weaknesses
Information silos leading to duplicated information, inconsistent formatting and style across documents, lack of version control for important documents leading to confusion.
Knowledge Base Content Strategy
A comprehensive content strategy is essential for creating, managing, and maintaining a knowledge base. This involves planning, creating, and reviewing content to ensure accuracy, consistency, and relevance. A content creation workflow should include stages such as topic ideation, content drafting, editing, review, and publication. Editorial guidelines should ensure consistency in style, tone, and formatting. A regular content review process ensures content remains accurate and up-to-date.
A flowchart depicting this lifecycle would illustrate the iterative nature of content creation and management.
Accessibility in Knowledge Base Design
Designing an accessible knowledge base ensures inclusivity for users with disabilities. Adherence to WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) is crucial. This involves using appropriate headings, alternative text for images, keyboard navigation, and sufficient color contrast. Search functionality should be accessible through assistive technologies.
| WCAG Success Criterion | Description | Knowledge Base Application |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1.1 Non-text Content | All non-text content must have text alternatives that convey the equivalent information. | Provide alternative text for all images and multimedia content. |
| 2.4.4 Link Purpose (In Context) | The purpose of each link can be determined from the link text alone. | Use descriptive link text that clearly indicates the destination. |
| 3.3.1 Error Prevention | Errors should be prevented whenever possible. | Use input validation to prevent errors in forms and searches. |
| 4.1.2 Name, Role, Value | For all user interface components, name, role, and value can be programmatically determined. | Ensure all interactive elements have appropriate ARIA attributes. |
Customizing the Genesys Knowledge Base
The Genesys Knowledge Base offers extensive customization options to align its functionality and appearance with specific business needs and branding guidelines. This allows organizations of all sizes, from small startups to large multinational corporations, to create a knowledge base that seamlessly integrates with their existing systems and enhances the user experience. Effective customization ensures a more efficient and engaging knowledge base, leading to improved agent and customer satisfaction.
Customization Options for Diverse Business Needs
The level and type of customization required will vary depending on the organization’s size and complexity. A large multinational corporation might require extensive customization, including multi-lingual support, complex role-based access controls, and integration with numerous internal systems. In contrast, a small startup might prioritize a simpler, more streamlined approach, focusing on branding consistency and ease of use. Genesys offers several customization options to cater to these varying needs.
- Search Functionality: Customization options include refining search algorithms to prioritize specific s, implementing synonym management, and configuring advanced search filters based on article metadata (e.g., product category, language, date). This ensures users quickly find the information they need, regardless of their search query phrasing. Benefits include improved search accuracy and faster knowledge access.
- Article Categorization: The ability to create custom categories and subcategories allows organizations to structure their knowledge base logically, reflecting their internal organizational structure or product hierarchy. This improves knowledge organization and retrieval. Benefits include improved knowledge organization and easier navigation.
- User Permissions: Granular control over user access allows organizations to restrict access to sensitive information based on roles or departments. This ensures data security and confidentiality. Benefits include enhanced security and compliance with data privacy regulations.
- API Access: The Genesys Knowledge Base API provides developers with extensive capabilities to integrate custom functionalities and data sources. This enables advanced customization beyond the standard interface. Benefits include enhanced flexibility and integration with other systems.
Tailoring the Knowledge Base to Company Branding
Maintaining brand consistency is crucial for creating a cohesive and professional user experience. Genesys allows for extensive customization of the knowledge base’s visual elements to match company branding guidelines.
- Color Scheme, Fonts, and Logos: The knowledge base can be customized to use the company’s specific colors, fonts, and logo. This ensures visual consistency with other company materials. Benefits include improved brand recognition and a more professional appearance.
- Header, Footer, and Sidebars: These elements can be customized to include company branding, navigation menus, and other relevant information. This provides a consistent brand experience across all sections of the knowledge base. Benefits include improved navigation and brand reinforcement.
- Custom CSS and JavaScript: Advanced users can use custom CSS and JavaScript to further tailor the appearance and functionality of the knowledge base. This allows for highly specific and detailed customization. Benefits include maximum control over visual design and functionality.
Integrating Custom Applications and Functionalities
Genesys Knowledge Base supports the integration of various custom applications and functionalities to extend its capabilities and enhance the user experience.
- Integration Methods: Genesys supports several integration methods, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The choice of method depends on the complexity of the application and the technical expertise available.
| Integration Method | Pros | Cons | Technical Requirements | Security Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| API | Flexible, scalable, powerful | Requires development expertise | API Key, Authentication Protocol | Data encryption, access control |
| Widgets | Easy to implement, visually appealing | Limited functionality, vendor dependence | Widget code, embedding instructions | Secure hosting, trusted sources |
| Iframes | Simple integration | Security risks if not properly secured | URL of the external application | CORS configuration, iframe sandboxing |
Common Customization Options and Their Benefits, Genesys knowledge base
The following list categorizes common customization options and their associated benefits:
Search Customization
- Custom Search Algorithms: Tailoring search algorithms to prioritize specific s and phrases. Benefits: Improved search accuracy, faster knowledge retrieval.
- Synonym Management: Defining synonyms to ensure users find information regardless of terminology used. Benefits: Enhanced search coverage, improved user experience.
Appearance Customization
Functionality Customization
User Experience Customization
Step-by-Step Guide: Changing the Knowledge Base Logo
This example demonstrates changing the knowledge base logo. Specific steps may vary based on the Genesys Knowledge Base version and configuration. Consult the official Genesys documentation for detailed instructions.
1. Access the Administration Panel
Log in to the Genesys Knowledge Base administration interface.
2. Navigate to Branding Settings
Find the section dedicated to branding or customization.
Genesys knowledge base systems are crucial for efficient customer service, providing agents with readily accessible information. Proficiency in navigating and utilizing such systems is increasingly vital, highlighting the importance of a skill like knowledge base as a job skill , making candidates more competitive. Mastering Genesys knowledge bases directly translates to improved performance and faster resolution times for customer inquiries.
3. Upload New Logo
Locate the option to upload a new logo image. Ensure the image is in the correct format and size as specified in the documentation.
4. Save Changes
Save the changes made to the branding settings.
5. Verify Changes
Access the knowledge base as a user to verify that the new logo is displayed correctly.
Managing and Updating Customizations
After deploying customizations, regular monitoring and updates are essential. Maintain a detailed record of all changes, including dates, authors, and descriptions. Version control systems can be invaluable for managing customizations effectively. For rolling back changes, consider using a staging environment to test updates before deploying them to the production environment. Regular backups are also highly recommended.
Troubleshooting Common Customization Issues
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: My custom CSS is not applying correctly. A: Check for syntax errors in your CSS code. Ensure the CSS file is correctly linked in the knowledge base’s settings. Clear your browser cache and try again.
- Q: My custom widget is not displaying. A: Verify the widget code is correctly implemented and the necessary dependencies are included. Check the widget’s documentation for troubleshooting tips.
- Q: I am encountering API integration errors. A: Verify your API key and authentication details. Check the API documentation for error codes and their explanations.
Genesys Knowledge Base Support Resources
[Insert links to relevant Genesys Knowledge Base documentation, tutorials, and support forums here.]
Troubleshooting Common Issues

This section addresses common problems encountered when using the Genesys Knowledge Base and provides practical solutions for resolving them. Understanding these troubleshooting steps will minimize downtime and ensure efficient knowledge access for agents and customers. The solutions are organized for ease of navigation and reference.
Search Functionality Issues
Ineffective search results are a frequent challenge. This can stem from various factors, including inaccurate usage, insufficient indexing, or issues with the search engine itself. Understanding the underlying cause is crucial for effective troubleshooting.
- Problem: No results returned for a relevant search query.
- Solution: Review the search query for typos and refine s. Try alternative phrasing or synonyms. If the problem persists, check the Genesys Cloud administrator interface to ensure the knowledge base is properly indexed and that the search engine is functioning correctly. Contact Genesys support if necessary.
- Problem: Too many irrelevant results are returned.
- Solution: Refine the search query using more specific s or Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT). Consider using filters available within the search interface to narrow the results based on criteria such as date, author, or category.
- Problem: Search results are slow to load.
- Solution: Check your internet connection. If the problem persists across multiple networks, contact Genesys support to investigate potential server-side issues or indexing problems.
Knowledge Article Access Problems
Agents and customers may encounter difficulties accessing specific knowledge articles. This may be due to permissions, broken links, or article unavailability.
- Problem: Unable to access a specific knowledge article due to permission restrictions.
- Solution: Verify user permissions within the Genesys Cloud administrator interface. Ensure the user has the necessary roles and permissions to access the desired knowledge article or knowledge base category.
- Problem: Encountering broken links within knowledge articles.
- Solution: Report the broken link through the designated feedback mechanism within the Genesys Knowledge Base. This allows Genesys administrators to address and repair the link.
- Problem: Knowledge article is unavailable or marked as outdated.
- Solution: Check if an updated version of the article exists. If not, contact the knowledge base administrator to request an update or clarification.
Integration Issues with Genesys Cloud
Seamless integration with the Genesys Cloud platform is crucial. Problems in this area can severely impact agent efficiency.
- Problem: Knowledge Base articles are not displaying correctly within the Genesys Cloud agent desktop.
- Solution: Verify the integration settings within the Genesys Cloud administrator interface. Ensure the Knowledge Base is correctly configured and connected to the agent desktop. Check for any error messages or logs related to the integration.
- Problem: Slow loading times for knowledge articles within the Genesys Cloud agent desktop.
- Solution: Check the network connection and investigate potential performance bottlenecks. Contact Genesys support to analyze server-side performance and investigate potential network issues.
Utilizing Genesys Support Resources
For complex issues not resolved through the above steps, effective utilization of Genesys support resources is essential.
When contacting Genesys support, provide detailed information including error messages, screenshots, and steps taken to troubleshoot the issue. This will enable a faster and more accurate resolution. Genesys typically offers various support channels such as phone, email, and online communities. Leverage the Genesys knowledge base itself to search for existing solutions to similar problems before contacting support.
Future Trends in Genesys Knowledge Base Technology

The Genesys Knowledge Base is poised for significant evolution in the next 3-5 years, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and improved user interface design. These changes will directly enhance both customer service agent efficiency and the customer self-service experience, leading to improved customer satisfaction and reduced operational costs. This section analyzes these emerging trends and their impact on the Genesys Knowledge Base.
Emerging Trends in Knowledge Base Technology
Several key trends are shaping the future of knowledge base technology. Understanding these trends is crucial for anticipating and adapting to the evolving needs of both agents and customers. The following table details five prominent trends and their potential impact on the Genesys Knowledge Base.
| Trend | Description | Impact on Genesys KB | Potential Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI-powered Search | Utilizing artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to understand the intent behind search queries, rather than simply matching s. | Significantly improved search accuracy and speed, leading to faster resolution times for agents and customers. Reduced reliance on precise matching. | Integration of natural language processing (NLP) and semantic search capabilities into the Genesys Knowledge Base search engine. Implementation of AI-powered query suggestion and auto-correction features. |
| Hyper-personalization | Tailoring knowledge base content and search results to individual users based on their role, past interactions, and preferences. | Improved customer experience through relevant and targeted information. Increased agent efficiency by providing contextually relevant information. | Leveraging customer data and interaction history to personalize search results and recommend relevant articles. Implementing personalized dashboards and content recommendations within the agent desktop and self-service portal. |
| Integration with Conversational AI | Seamless integration of the knowledge base with chatbots and virtual assistants to provide instant answers to customer queries. | Enhanced self-service capabilities, reducing the workload on agents. Improved customer satisfaction through immediate and accurate responses. | Developing APIs to allow chatbots to directly access and retrieve information from the Genesys Knowledge Base. Enabling chatbots to seamlessly transfer complex queries to human agents with relevant knowledge base articles pre-loaded. |
| Proactive Knowledge Delivery | Anticipating customer needs and proactively delivering relevant knowledge base articles before a query is even made. | Reduced customer wait times and improved first contact resolution rates. Improved agent efficiency through preemptive information provision. | Using machine learning to identify patterns in customer interactions and proactively suggest relevant articles to agents. Implementing proactive notifications and recommendations within the self-service portal based on customer behavior. |
| Enhanced Knowledge Authoring Tools | Providing agents and knowledge managers with intuitive and user-friendly tools for creating, updating, and managing knowledge base content. | Improved content quality and consistency. Reduced time and effort required for content creation and maintenance. | Implementing AI-assisted writing tools to suggest improvements to content clarity and accuracy. Providing collaborative editing features to streamline content updates. |
Impact on Genesys Knowledge Base Functionalities
The emerging trends described above will significantly impact several core functionalities of the Genesys Knowledge Base.
Search Functionality
AI-powered search, utilizing NLP and semantic search, will drastically improve search accuracy and efficiency. The system will understand the intent behind queries, even if they are phrased informally or contain misspellings. Personalized search results will further enhance the experience by prioritizing articles relevant to the user’s context.
Content Management
AI-assisted authoring tools will streamline content creation, suggesting improvements in grammar, style, and clarity. Collaborative editing features will enable multiple authors to work simultaneously, improving efficiency and consistency. Automated version control will ensure that the most up-to-date information is always available.
Agent Assistance
Real-time suggestions and context-aware recommendations will provide agents with the precise information they need during customer interactions. Integrated knowledge access within the agent desktop will eliminate the need to switch between applications, streamlining workflows.
Self-Service Portal
Improved navigation, personalized content delivery, and integration with chatbots will enhance the customer self-service experience. Customers will find the information they need quickly and easily, reducing their reliance on agents for simple queries.
Predictions and Future Direction
Based on the identified trends, several predictions can be made regarding the future direction of the Genesys Knowledge Base.
Prediction 1: Within three years, AI-powered search will become the standard, significantly reducing the reliance on -based searches and improving search accuracy by at least 50%, because advancements in NLP and machine learning will enable the system to understand the nuanced meaning of user queries, even with variations in phrasing. This is supported by the current rapid advancements in AI-driven search technology seen in other sectors like e-commerce.
Prediction 2: The Genesys Knowledge Base will increasingly adopt a headless architecture, allowing for greater flexibility and integration with other platforms and applications, because the demand for omnichannel customer service will necessitate seamless knowledge access across various touchpoints. Companies like Shopify have successfully implemented headless architectures to support diverse front-end experiences.
Prediction 3: Complete integration with Genesys Cloud’s other products, such as routing and analytics, will become a core feature, providing a holistic view of customer interactions and enabling proactive service improvements, because this integrated approach allows for real-time analysis of customer needs and enables the system to anticipate and address issues before they escalate. This aligns with the industry-wide trend towards unified customer experience platforms.
Innovative Features for Future Genesys Knowledge Base Versions
Several innovative features could significantly enhance the Genesys Knowledge Base.
- Automated Content Translation: Automatically translate knowledge base articles into multiple languages, expanding accessibility and improving global customer support. This would reduce translation costs and improve time-to-market for multilingual support.
- Sentiment Analysis: Analyze customer feedback within the knowledge base to identify areas for improvement in content or service. This would allow for data-driven content optimization and proactive issue resolution.
- Knowledge Graph Integration: Integrate a knowledge graph to enhance search capabilities and enable more complex queries and relationship discovery within the knowledge base. This allows for more contextual and accurate search results.
- Gamification of Knowledge Base Use: Implement reward systems for agents and customers who actively use and contribute to the knowledge base. This fosters a culture of knowledge sharing and continuous improvement.
- Predictive Knowledge Base Analytics: Utilize machine learning to predict future knowledge needs based on historical data and current trends. This allows for proactive content creation and reduces the need for reactive updates.
Limitations and Challenges
Implementing these predicted trends and features will present challenges. Technological hurdles include the need for robust AI and machine learning infrastructure. Cost considerations include the investment in new software, training, and ongoing maintenance. Resistance to adoption may arise from agents and knowledge managers accustomed to traditional methods. Addressing these challenges through phased implementation and comprehensive training will be crucial for successful adoption.
Case Studies of Successful Genesys Knowledge Base Implementations
This section details successful Genesys Knowledge Base implementations across diverse industries, highlighting lessons learned, best practices, and the positive impact on customer service. We will examine how organizations tailored the Genesys Knowledge Base to meet their specific operational needs and achieve measurable improvements in efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Genesys Knowledge Base Implementation at a Large Financial Institution
A major multinational bank implemented the Genesys Knowledge Base to centralize and standardize its vast repository of customer support information. Previously, information was scattered across various departments and systems, leading to inconsistent responses and prolonged resolution times. The implementation involved migrating existing documentation, developing a robust content management strategy, and integrating the Knowledge Base with the bank’s existing Genesys Cloud contact center platform.
This resulted in a 25% reduction in average handle time for customer inquiries and a 15% increase in customer satisfaction scores, as measured through post-call surveys. The bank also saw a significant reduction in agent training time due to the easily accessible and consistently updated knowledge base. The implementation leveraged role-based access control to ensure data security and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Improved Customer Onboarding with Genesys Knowledge Base in a SaaS Company
A Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) company utilized the Genesys Knowledge Base to streamline its customer onboarding process. Before implementation, onboarding relied heavily on individual agent interaction, resulting in inconsistencies and high support costs. By creating a comprehensive knowledge base with interactive tutorials, FAQs, and troubleshooting guides, the company significantly reduced the number of support tickets related to onboarding. The self-service capabilities empowered customers to resolve issues independently, freeing up agents to handle more complex requests.
This resulted in a 30% decrease in support tickets and a 10% improvement in customer retention rates. The company also used the Knowledge Base’s analytics features to identify areas for improvement in the onboarding process and continuously refine its content.
Enhanced Technical Support with Genesys Knowledge Base in a Telecommunications Provider
A large telecommunications provider implemented the Genesys Knowledge Base to improve its technical support capabilities. The company faced challenges with inconsistent troubleshooting procedures and a lack of readily available information for its agents. The implementation involved creating a structured knowledge base with detailed troubleshooting guides, diagrams, and videos. This allowed agents to quickly access the information they needed to resolve customer issues efficiently.
The result was a 20% reduction in average resolution time for technical support inquiries and a significant increase in first-call resolution rates. The company also benefited from improved agent morale due to the increased efficiency and reduced frustration associated with searching for information. The implementation included a robust search functionality, ensuring agents could quickly find relevant information regardless of the s used.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
Successful Genesys Knowledge Base implementations emphasize meticulous planning, comprehensive content strategy, and ongoing maintenance. Key lessons learned include the importance of strong executive sponsorship, dedicated resources for content creation and management, and continuous monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs) such as average handle time, first-call resolution rates, and customer satisfaction scores. Best practices include the use of a phased rollout approach, incorporating feedback from agents and customers, and regular content updates to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Furthermore, integrating the Knowledge Base with other customer service tools and systems is crucial for maximizing its effectiveness.
Comparison with Alternative Knowledge Base Solutions
Selecting the optimal knowledge base solution requires a thorough comparison of available options. This section analyzes Genesys Knowledge Base against prominent competitors, highlighting key distinctions and similarities to aid in informed decision-making. The analysis considers factors crucial for effective knowledge management within a contact center environment.
Key Differences and Similarities Among Knowledge Base Solutions
Genesys Knowledge Base, while a robust solution integrated directly within the Genesys Cloud ecosystem, differs from standalone knowledge bases in its seamless integration capabilities and focus on contact center optimization. Standalone solutions, such as Zendesk Guide, Salesforce Knowledge, and Guru, offer broader functionality in areas like content creation and collaboration but may require more extensive integration efforts to connect with a contact center platform.
Similarities across all solutions include core features such as search functionality, article management, and version control. However, the depth and sophistication of these features can vary considerably.
Comparison Table of Knowledge Base Solutions
| Feature | Genesys Knowledge Base | Zendesk Guide | Salesforce Knowledge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genesys Cloud Integration | Seamless, native integration | Requires integration via API or third-party tools | Requires integration via API or third-party tools |
| Pricing | Tiered pricing based on Genesys Cloud subscription | Tiered pricing based on features and users | Tiered pricing based on features and users |
| Search Functionality | Robust search with AI-powered suggestions | Robust search with various filtering options | Robust search with advanced filtering and personalization |
| Reporting and Analytics | Integrated reporting within Genesys Cloud analytics dashboard | Customizable reporting features | Customizable reporting features with Salesforce ecosystem integration |
| Collaboration Features | Collaboration features within Genesys Cloud | Strong collaboration features with commenting and version history | Collaboration features integrated with Salesforce Chatter |
| Ease of Use | Intuitive interface for agents and administrators | Generally user-friendly interface | Can be complex for non-Salesforce users |
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Knowledge Base Solution
The selection of a knowledge base solution hinges on several critical factors. These factors encompass budget constraints, existing infrastructure, scalability requirements, and the specific needs of the organization.
Budgetary considerations are paramount. Solutions range from cost-effective options suitable for small businesses to enterprise-grade solutions with higher price tags. The existing IT infrastructure and its compatibility with the chosen solution are also crucial. Seamless integration with existing CRM and contact center systems is essential to avoid disruptions and optimize workflow. Scalability ensures the solution can adapt to future growth and evolving business needs.
Finally, the specific requirements of the organization, including the volume of content, the complexity of the knowledge base, and the number of users, should all inform the selection process.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the pricing model for Genesys Knowledge Base?
Pricing varies depending on factors such as the number of users, storage needs, and specific features utilized. Contact Genesys directly for a customized quote.
Can I integrate the Genesys Knowledge Base with third-party applications outside the Genesys ecosystem?
Integration with third-party applications may be possible depending on their APIs and capabilities. Consult Genesys documentation or support for specific compatibility information.
How does Genesys ensure data backup and recovery in case of a system failure?
Genesys employs redundant systems and regular data backups to minimize data loss. Specific backup frequencies and retention policies should be clarified with Genesys support.
What training resources are available for Genesys Knowledge Base administrators?
Genesys offers comprehensive training materials, including video tutorials, online courses, and PDF guides, tailored to different user roles. Access to these resources is typically available through the Genesys customer portal.
What are the system requirements for the Genesys Knowledge Base?
System requirements depend on the deployment method (cloud or on-premise). Consult Genesys documentation for detailed specifications regarding browser compatibility, server requirements, and network infrastructure needs.


