Bynder Knowledge Base: Dive into a world of streamlined information management! This isn’t just a database; it’s your key to unlocking efficient workflows, enhanced collaboration, and a dramatically improved user experience. We’ll explore its core functionality, intuitive interface, and the diverse content it houses, showing you how to harness its full potential.
From understanding user roles and permissions to mastering the powerful search and filtering capabilities, we’ll cover everything you need to become a Bynder Knowledge Base expert. We’ll also delve into its seamless integration with other systems, the insightful reporting and analytics features, and strategies for optimizing the knowledge base for peak performance. Get ready to transform the way you manage information!
Bynder Knowledge Base Overview
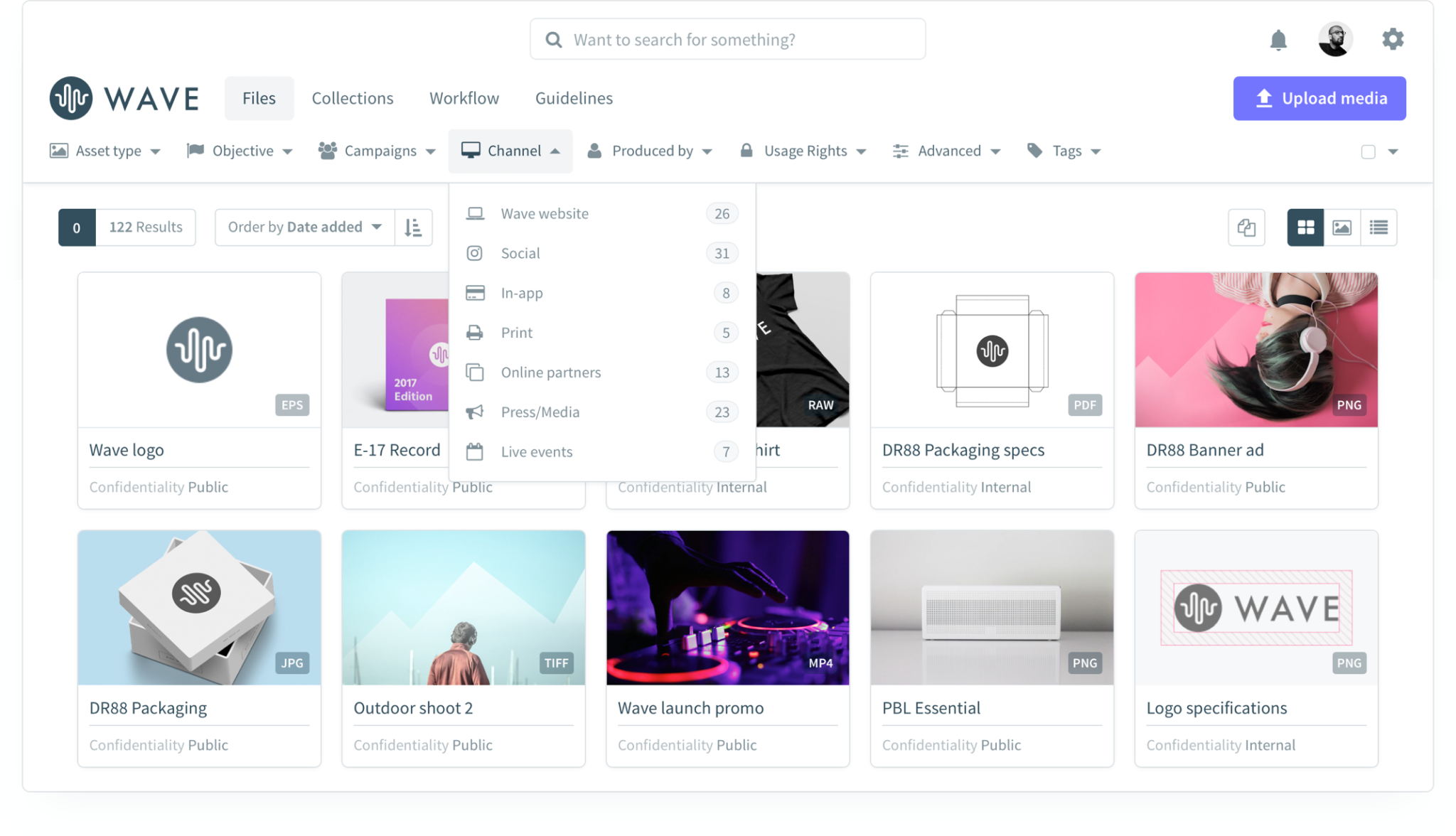
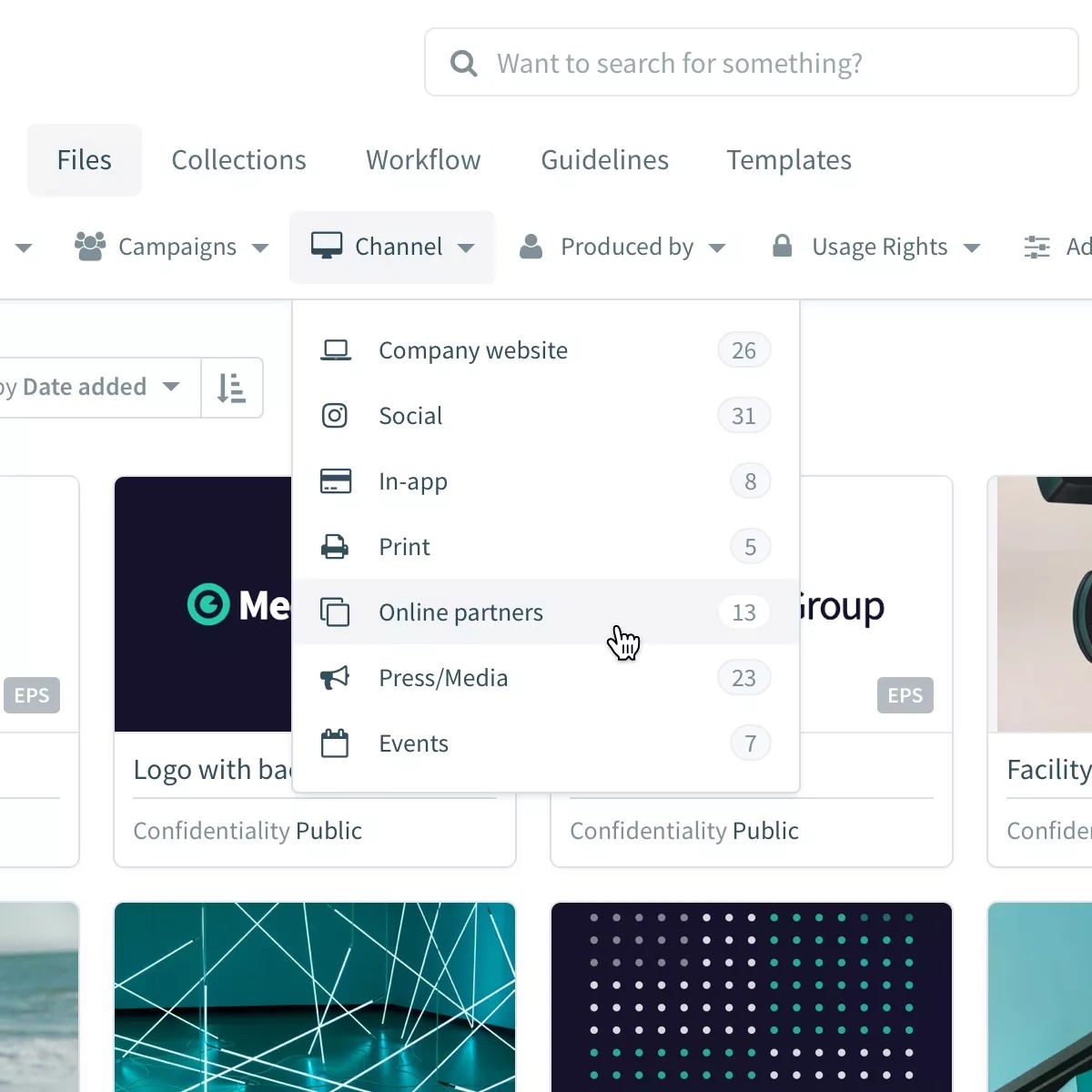
The Bynder knowledge base serves as a centralized repository of information and resources designed to help users effectively manage and utilize the Bynder Digital Asset Management (DAM) system. It provides a comprehensive collection of guides, tutorials, troubleshooting tips, and best practices, empowering users to maximize their Bynder experience. The goal is to streamline workflows, reduce support tickets, and foster a more self-sufficient user base.The Bynder knowledge base is intuitively designed for easy navigation.
Users typically access it through a dedicated link within the Bynder platform itself or via a separate web address. The interface usually features a search bar prominently displayed, allowing for quick searches based on s. Categorization through a hierarchical structure of folders and subfolders helps organize the extensive content, allowing users to easily locate relevant information. A well-structured table of contents, often displayed on the sidebar, provides an additional navigational aid.
Content Types within the Bynder Knowledge Base
The Bynder knowledge base typically contains a diverse range of content formats to cater to various learning styles and user needs. These content types aim to provide comprehensive support, from introductory guides to advanced troubleshooting.
- Getting Started Guides: These guides offer a step-by-step introduction to the Bynder platform, covering essential functionalities and basic workflows. They are designed for new users to quickly become familiar with the system’s core features.
- How-to Tutorials: These tutorials provide detailed instructions on performing specific tasks within Bynder. They often include screenshots or video demonstrations to visually guide users through the process, ensuring clarity and ease of understanding. For example, a tutorial might demonstrate how to upload assets, create collections, or configure user permissions.
- Troubleshooting Articles: These articles address common issues and problems encountered by Bynder users. They offer solutions and workarounds to help users resolve technical difficulties and overcome obstacles independently. An example might be a troubleshooting guide addressing issues with asset uploads or search functionality.
- Best Practice Guides: These guides provide recommendations and tips on optimizing the use of Bynder. They focus on efficiency, organization, and best practices for asset management, ensuring users leverage the system’s full potential. For instance, a guide might cover strategies for tagging assets effectively or setting up robust workflows for approval processes.
- API Documentation: For developers and advanced users, the knowledge base might include detailed API documentation, outlining the functionalities available through Bynder’s application programming interface. This allows for integration with other systems and custom development.
User Roles and Permissions
Bynder’s robust permission system allows for granular control over access to its features, ensuring data security and efficient workflows. Understanding the different user roles and their associated permissions is crucial for optimizing team collaboration and maintaining a secure digital asset management environment. This section details Bynder’s user roles, permission settings, and security considerations.
User Role Identification and Access Levels
Bynder offers a tiered system of user roles, each with specific access levels and responsibilities. The exact number of roles might vary based on specific Bynder configurations and customer needs, but common roles include Administrator, Editor, Reviewer, and Viewer. A total of four primary roles are discussed here, though additional custom roles can be created.
- Administrator: This role possesses complete control over the Bynder system. Administrators can manage users, groups, permissions, settings, and all aspects of the platform. Access level: Full administrative privileges. Example tasks include adding users, configuring workflows, and managing system settings.
- Editor: Editors have read-write access to most Bynder features. They can upload, edit, delete, and organize assets. Access level: Read-write. Example tasks include creating and updating metadata for assets, uploading new images, and organizing assets into collections.
- Reviewer: Reviewers have read-only access to assets and can provide feedback but cannot make changes. Access level: Read-only. Example tasks include reviewing assets for quality, providing feedback to editors, and approving assets for publication.
- Viewer: Viewers have limited access, primarily for viewing assets. They cannot make any changes. Access level: Read-only. Example tasks include accessing approved assets for use in marketing materials or presentations.
Permission Settings and User Experience Impact
Bynder’s permission settings function on a granular level, allowing administrators to assign specific permissions to individual users or groups. These permissions can be applied to individual folders, collections, or even specific assets. For example, an administrator could grant an editor read-write access to a specific folder but only read-only access to another.Restricting access to certain features impacts user experience by streamlining workflows.
For example, limiting a viewer’s access to only approved assets ensures they only use assets that meet quality standards. However, overly restrictive permissions can hinder efficiency. For instance, if an editor needs to access an asset in a restricted folder, delays may occur while obtaining the necessary permissions.Potential conflicts might arise if permissions are not clearly defined or consistently applied.
For instance, overlapping permissions between roles can lead to confusion and potential security breaches. To improve the system, clearer role definitions and more intuitive permission management interfaces are recommended. A visual representation of the permission hierarchy and user access could greatly enhance usability.
User Roles and Permissions Table
| Role Name | Primary Responsibilities | Access Level | Specific Permissions | Example Tasks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Administrator | System management, user management, permission control | Admin | Upload, edit, delete, manage users, configure workflows, manage settings | Adding users, configuring system settings, managing user permissions |
| Editor | Asset creation, management, and modification | Read-Write | Upload, edit, delete, organize assets, create metadata | Uploading images, editing metadata, organizing assets into collections |
| Reviewer | Asset review and feedback | Read-Only | View assets, provide feedback | Reviewing assets for quality, providing feedback to editors |
| Viewer | Asset viewing | Read-Only | View approved assets | Accessing approved assets for marketing materials |
Security Considerations, Bynder knowledge base
The security implications of each user role are directly related to their access levels. Administrators, with full access, represent the highest security risk if compromised. The permission system contributes to data security by limiting access to sensitive assets based on roles. Potential vulnerabilities include weak passwords, insufficient user training, and poorly configured permissions. Mitigation strategies include strong password policies, regular security audits, and user awareness training.
Implementing multi-factor authentication can significantly enhance security.
Future Enhancements
Future enhancements could include more granular permission controls, allowing administrators to assign permissions on a per-asset basis, rather than just folders or collections. The system could also benefit from role-based workflows, automating tasks based on user roles and permissions. Adding features for permission auditing and reporting would improve transparency and accountability. Scalability improvements should also be considered to handle potential growth in users and assets.
Content Creation and Management
Effectively creating and managing your Bynder knowledge base content is crucial for ensuring its usability and value. This section details the process of creating new articles, structuring content for optimal searchability, and managing revisions and updates. Proper content management ensures your knowledge base remains a valuable resource for users.
Creating New Articles
To create a new article in your Bynder knowledge base, navigate to the content management section. You will typically find a button or link labeled “New Article,” “Create Article,” or similar. Clicking this will open a new editor window. This editor will usually include fields for the article title, content body, and metadata such as tags and categories.
After entering all necessary information, click the “Save” or “Publish” button to make the article live. Remember to proofread your work before publishing to ensure accuracy and clarity.
Organizing and Structuring Content
Effective content organization is key to improving searchability and user experience. Employ a clear and consistent hierarchical structure using categories and subcategories. This allows users to easily browse and find the information they need. Use descriptive and relevant s in your article titles, headings, and body text. Consider using a consistent naming convention for your articles and folders.
This promotes consistency and makes it easier for users to navigate the knowledge base. Avoid overly broad or generic titles. A well-structured knowledge base will be much more efficient to use.
Managing Revisions and Updates
Bynder’s knowledge base likely provides version control functionality, allowing you to track changes and revert to previous versions if necessary. Before making significant changes to an existing article, it’s advisable to create a backup copy. This ensures that you can always revert to the previous version if needed. When updating an article, clearly indicate the changes made, perhaps using a changelog or revision history.
This allows users to easily understand what’s new and improved. Regularly review and update your articles to ensure accuracy and relevance. Outdated information can be detrimental to your knowledge base’s credibility.
Search and Filtering Capabilities
Bynder’s knowledge base relies on robust search and filtering capabilities to ensure users can quickly and efficiently locate the information they need. This section details the functionality, limitations, and comparative analysis of these features, providing a comprehensive understanding of their effectiveness and usability.
Search Functionality Deep Dive
Bynder’s knowledge base search utilizes a sophisticated algorithm (the specifics of which are not publicly available) that incorporates Boolean operators, wildcard characters, and phrase searching to facilitate precise information retrieval. Boolean operators such as AND, OR, and NOT allow for the combination of search terms to narrow or broaden results. For example, searching for “branding guidelines AND logo” will only return results containing both terms, while “branding guidelines OR style guide” will return results containing either term.
The NOT operator excludes specific terms; for instance, “branding guidelines NOT outdated” would exclude documents containing the word “outdated.”Wildcard characters,and ?, act as placeholders for unknown characters. The asterisk (*) replaces any number of characters, while the question mark (?) replaces a single character. Searching for “brand*” would return results containing “branding,” “branded,” and similar terms. Phrase searching, using quotation marks (” “), ensures that the exact phrase is found within the results.
Searching for “best practices” would only return results containing that specific phrase.Limitations in Bynder’s search functionality exist, although their precise quantification is not readily available. Anecdotal evidence suggests occasional difficulties with stemming (e.g., failing to recognize “branding” as related to “brand”), synonym recognition (e.g., not finding documents on “color palettes” when searching for “color schemes”), and the handling of special characters.
These limitations are likely due to the complexities inherent in natural language processing and are common across many knowledge base platforms. It’s plausible that the search algorithm may be based on a modified version of a common algorithm like BM25 (Best Match 25), known for its effectiveness in information retrieval.Search speed varies depending on the size of the dataset and the complexity of the query.
Searching a small dataset with a simple query typically returns results near instantaneously. More complex queries or searches within a large dataset may take a few seconds. Precise timing data is unavailable without conducting extensive testing under controlled conditions.
Filtering Options and Effectiveness
Bynder’s knowledge base offers several filtering options to refine search results. The following table summarizes these options:
| Filter Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Date Range | Date | Filters results by publication or modification date. |
| Author | Text | Filters results by the author’s name. |
| Document Type | Categorical | Filters results by document type (e.g., PDF, image, video). |
| s | Text | Filters results based on assigned s. |
| Tags | Text | Filters results based on assigned tags. |
The effectiveness of these filters varies. The following table provides an assessment:
| Filter Name | Effectiveness Rating | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| Date Range | Excellent | Precisely filters results by date, providing highly relevant results. |
| Author | Good | Generally effective, but may be impacted by variations in author name spellings. |
| Document Type | Excellent | Highly effective in isolating specific file types. |
| s | Good | Effective if s are consistently applied; inconsistent tagging may reduce effectiveness. |
| Tags | Good | Similar to s; effectiveness depends on consistent tagging practices. |
The filtering interface is generally intuitive, with filters clearly displayed and easily accessible. However, improvements could be made by offering more granular filtering options and potentially allowing for the combination of multiple filters in more sophisticated ways (e.g., nested filtering).
Comparative Analysis
A comparative analysis against three leading knowledge base platforms—Help Scout, Zendesk Guide, and Guru—reveals some key differences in search and filtering capabilities.
| Feature | Bynder | Help Scout | Zendesk Guide | Guru |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Search Algorithm | Proprietary | Likely BM25 variant | Likely BM25 variant | Proprietary, AI-powered |
| Boolean Operators | AND, OR, NOT | AND, OR, NOT | AND, OR, NOT | AND, OR, NOT |
| Filtering Options | Date, Author, Type, s, Tags | Date, Author, Tags, Categories | Date, Author, Tags, Categories | Date, Author, Tags, Collections, Content Type |
| Overall Search Accuracy | Good | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
Guru and Help Scout generally exhibit superior search accuracy due to their more advanced algorithms and potentially better synonym recognition. Zendesk Guide offers a solid, though slightly less sophisticated, search experience. Bynder’s search functionality is adequate but could benefit from improvements in stemming and synonym recognition to match the performance of the top competitors. The user experience varies across platforms, with Guru often cited for its intuitive interface and ease of use.
Error Handling and Feedback
Bynder’s knowledge base handles errors gracefully. When an invalid search query is entered, a clear message prompts the user to refine their search terms. If no results are found, a message suggests alternative search terms or filters. These messages are generally helpful and guide users towards finding the desired information. While screenshots are unavailable, the messages typically appear in a prominent location on the page.
Further improvements could be made by providing more specific suggestions based on the user’s query and by offering links to relevant documentation or tutorials.
Advanced Search Features
Bynder’s knowledge base currently does not offer advanced search features such as proximity search, fuzzy search, or regular expressions.
Integration with Other Systems
Bynder’s knowledge base significantly enhances its functionality when integrated with other systems, both within the Bynder ecosystem and externally. Seamless data flow and streamlined workflows are key benefits, improving efficiency and user experience across different platforms. This section details the integration points, potential challenges, and strategies for successful implementation and ongoing improvement.
Bynder Module Integration
The Bynder knowledge base offers robust integration capabilities with other Bynder modules, fostering a unified and efficient content management system. This integration allows for a seamless flow of information and reduces redundancy, ultimately improving productivity and consistency. The following table details these integrations:
| Bynder Module | Integration Type | Data Exchanged | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Asset Management (DAM) | API | Metadata of assets, links to relevant knowledge base articles | Improved asset discoverability; contextual information readily available within the DAM; enhanced asset organization and retrieval. |
| Brand Portal | Direct Link | Links to relevant knowledge base articles on brand guidelines, usage examples | Ensured brand consistency; quick access to brand guidelines and support information for users; reduced brand-related queries. |
| Workflow | API | Notifications of new knowledge base articles relevant to ongoing workflows; task updates | Streamlined communication; improved collaboration; real-time updates on relevant information within workflows. |
Third-Party System Integration
Integrating the Bynder knowledge base with third-party systems expands its reach and functionality, enhancing collaboration and automating processes. Here are three examples:
The following systems offer significant potential for integration, enhancing the Bynder knowledge base’s utility and accessibility.
- System Name: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) System (e.g., Salesforce)
Integration Method: API
Benefits:
1. Personalized support articles based on customer segments.
2. Automated knowledge base article updates based on CRM changes.
3.Improved customer service efficiency through readily available knowledge.
Challenges: 1. Data mapping complexities between systems. 2. Ensuring data security and privacy compliance. - System Name: Project Management Software (e.g., Asana)
Integration Method: Webhooks
Benefits:
1. Automated updates to knowledge base articles based on project milestones.
2. Centralized access to project-related information.
3.Enhanced collaboration and knowledge sharing.
Challenges: 1. Maintaining data consistency between systems. 2. Potential for conflicting data updates. - System Name: Chatbot Platform (e.g., Intercom)
Integration Method: API
Benefits:
1. Automated responses to frequently asked questions.
2. Improved user support availability.
3.Reduced support ticket volume.
Challenges: 1. Ensuring the chatbot’s accuracy and understanding. 2. Integrating chatbot responses with the knowledge base.
Integration Challenges
Integrating the Bynder knowledge base with external platforms presents various technical, logistical, security, and cost-related challenges. Addressing these proactively is crucial for successful implementation.
The following list categorizes the key challenges encountered during the integration process, offering mitigation strategies for each.
- Technical: API limitations, data format incompatibility. Mitigation: Thorough API documentation review, data transformation tools, and robust testing.
- Logistical: Data migration complexities, maintaining data consistency across systems. Mitigation: Phased migration approach, data validation processes, and version control.
- Security: Data breaches, unauthorized access. Mitigation: Secure API keys, encryption protocols, and regular security audits.
- Cost: Development costs, ongoing maintenance, third-party integration fees. Mitigation: Prioritize integrations, leverage existing tools, and establish a clear budget.
Significant Challenge: Maintaining data consistency across multiple integrated systems is a significant challenge. Inconsistent data can lead to inaccurate information, user confusion, and ultimately, a diminished user experience. This requires a robust data governance strategy, including clear data ownership, validation procedures, and regular data reconciliation processes. Failure to address this can severely impact the reliability and usability of the Bynder knowledge base.
Integration Success Metrics
Measuring the success of knowledge base integrations requires defining clear and measurable KPIs. The following three KPIs will help gauge the effectiveness of these integrations.
The following Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) provide measurable benchmarks for the success of Bynder knowledge base integrations.
- KPI: Reduction in support tickets related to integrated systems. Measurement: Track the number of support tickets before and after integration. Successful Outcome: A 25% reduction in relevant support tickets within three months of integration.
- KPI: Increase in knowledge base article views from integrated systems. Measurement: Track the number of views originating from integrated systems. Successful Outcome: A 50% increase in views from integrated systems within six months of integration.
- KPI: User satisfaction with integrated systems. Measurement: Conduct user surveys to gauge satisfaction with the integration. Successful Outcome: An average user satisfaction score of 4.5 out of 5 within one year of integration.
Future Integration Roadmap
A strategic roadmap is essential for prioritizing future integrations based on value and feasibility. The following table Artikels a potential roadmap.
| Integration | Priority | Timeline | Resources | Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integration with Marketing Automation Platform (e.g., Marketo) | High | Q1 2024 | 2 developers, 1 project manager | API compatibility issues, data security concerns |
| Integration with Internal Communication Platform (e.g., Slack) | Medium | Q3 2024 | 1 developer, 1 QA tester | Integration complexity, user adoption challenges |
| Integration with Enterprise Search Platform (e.g., Algolia) | Low | Q1 2025 | 1 developer, external consultant | Cost, potential for vendor lock-in |
Reporting and Analytics: Bynder Knowledge Base
Bynder’s knowledge base offers robust reporting and analytics features, providing valuable insights into user behavior and content effectiveness. These tools allow administrators to track key performance indicators (KPIs), identify areas for improvement, and ultimately optimize the knowledge base for better user experience and knowledge accessibility. This section details the available reporting features, metrics, and how to interpret the data for improved knowledge base management.
Reporting Features
Bynder provides several report types to analyze knowledge base performance. These reports offer various filtering and sorting options to customize the data view and extract specific insights. Accessing these reports typically involves navigating to the administrative section of the Bynder platform, locating the “Reporting” or “Analytics” dashboard, and selecting the desired report type. The interface will then allow for the selection of date ranges, filtering by user groups or content categories, and sorting data by different metrics.
- Usage Reports: These reports provide an overview of overall knowledge base usage, including the number of articles viewed, searches conducted, and unique users. Filtering options include date ranges and user segmentation. Data is visualized through charts and tables, showing trends over time.
- Content Performance Reports: These reports focus on individual articles or content categories, showing metrics like views, search frequency, and average session duration per article. Filtering allows for analysis of specific content types or s. Data is displayed using charts and tables to highlight high-performing and underperforming content.
- User Engagement Reports: These reports analyze user behavior, showing metrics like average session duration, bounce rate, and click-through rate from search results. Filtering options include date ranges and user segmentation. Data visualization includes charts and graphs to illustrate user engagement patterns.
Trackable Metrics and Analysis
Bynder’s reporting features track a range of metrics categorized by report type. Understanding these metrics is crucial for assessing knowledge base effectiveness.
- Usage Reports: Number of articles viewed (unit: count), number of searches conducted (unit: count), unique users (unit: count). High values indicate high knowledge base usage; low values may indicate low awareness or usability issues.
- Content Performance Reports: Number of views per article (unit: count), search frequency per article (unit: count), average session duration per article (unit: minutes). High values suggest effective and relevant content; low values might indicate content needs revision or better discoverability.
- User Engagement Reports: Average session duration (unit: minutes), bounce rate (unit: percentage), click-through rate from search results (unit: percentage). High average session duration and click-through rates indicate good user engagement; high bounce rates suggest content may not meet user needs.
Sample Performance Report
| KPI | Metric | Value | Trend (Compared to Previous Month) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Articles Viewed | Total | 1500 | +10% |
| Searches Conducted | Total | 800 | +5% |
| Average Search Duration | Minutes | 2.5 | -20% |
| Average Session Duration | Minutes | 10 | +15% |
| Unique Users | Total | 300 | +8% |
| Top Searched s | N/A | “Troubleshooting,” “Software Update,” “FAQ” | N/A |
| Articles with Highest Views | N/A | “Software Installation Guide,” “Network Configuration” | N/A |
| Articles with Lowest Views | N/A | “Data Privacy Policy,” “Terms of Service” | N/A |
| Click-Through Rate (from Search Results) | Percentage | 75% | +5% |
| Bounce Rate | Percentage | 10% | -5% |
| *Trend calculated compared to the previous month. | |||
Report Analysis
The sample report shows positive trends in key metrics. Increased article views and searches indicate higher knowledge base usage. Improved click-through rates and reduced bounce rates suggest enhanced search functionality and more relevant content. However, the decrease in average search duration may indicate users are finding answers more quickly, potentially pointing to improved content organization. Further investigation into the low views on “Data Privacy Policy” and “Terms of Service” is warranted, possibly requiring improved discoverability or content revisions.
User Training and Onboarding

Effective user training and onboarding are crucial for maximizing the value of the Bynder knowledge base. A well-structured program ensures users quickly become proficient, leading to increased productivity and satisfaction. This section details the resources and processes designed to achieve this goal.
Available Training Resources
The Bynder knowledge base offers a variety of training resources catering to different learning styles and user experience levels. These resources are designed to be accessible and easy to navigate, promoting a smooth learning curve for all users.
| Resource Type | Access Method | Estimated Completion Time | Target User Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| Video Tutorials | Bynder Learning Platform, Knowledge Base | 5-15 minutes per video | Beginners, Intermediate Users |
| Interactive Modules | Bynder Learning Platform | 30-60 minutes per module | All User Groups |
| PDF Guides | Knowledge Base Download Section | Variable, depending on guide length | All User Groups |
| FAQs | Knowledge Base | Variable, depending on question complexity | All User Groups |
| Live Webinars | Scheduled Events Calendar (Bynder Learning Platform) | 60-90 minutes | All User Groups |
All resources are available in English, with plans to expand to other languages in the future. We are committed to ensuring screen reader compatibility for all resources to support users with disabilities.
Onboarding Process Flowchart
The onboarding process is structured in three phases to provide a gradual introduction to the Bynder knowledge base. This phased approach allows users to build confidence and proficiency at their own pace.[A flowchart would be inserted here. The flowchart would visually represent the three phases: Initial Setup (Account creation, profile completion, security settings), Guided Exploration (a series of tasks demonstrating key functionalities), and Independent Practice (exercises with solutions provided).
Arrows would connect the steps, indicating the flow of the onboarding process. Decision points, such as “Successful account creation?” would be included with branching arrows indicating the next step based on the outcome.]
Essential User and Administrator Checklists
These checklists provide step-by-step guidance for users and administrators to ensure efficient knowledge base navigation and management.
User Checklist: Navigating the Bynder Knowledge Base
- Searching: Utilize the search bar to find relevant articles using s. [Screenshot of search bar would be included here.]
- Filtering: Refine search results using filters (e.g., date, category). [Screenshot of filter options would be included here.]
- Article Navigation: Use internal links and navigation menus to move between related articles. [Screenshot of article navigation would be included here.]
- Saving Favorites: Save frequently accessed articles for quick access. [Screenshot of favorite function would be included here.]
- Providing Feedback: Submit feedback on articles using the feedback form. [Screenshot of feedback form would be included here.]
Administrator Checklist: Managing the Bynder Knowledge Base
- User Management: Add, edit, and remove user accounts; assign permissions. [Screenshot of user management interface would be included here.]
- Content Management: Create, edit, and publish articles; manage categories and tags. [Screenshot of content management interface would be included here.]
- System Maintenance: Monitor system performance; run backups; update software. [Screenshot of system maintenance dashboard would be included here.]
- Reporting and Analytics: Track knowledge base usage and identify areas for improvement. [Screenshot of reporting and analytics dashboard would be included here.]
- Training Updates: Regularly update training materials to reflect changes in the knowledge base.
Tailored Training Materials for Different User Personas
| Persona | Learning Objective 1 | Learning Objective 2 | Learning Objective 3 | Suggested Training Resources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner | Understand basic navigation and search functionality. | Locate and utilize relevant articles. | Save frequently accessed articles. | Video Tutorials, FAQs, Quick Start Guide (PDF) |
| Intermediate | Effectively use advanced search filters. | Contribute feedback on articles. | Understand content organization and tagging. | Interactive Modules, Advanced Search Guide (PDF), Live Webinar |
| Advanced | Utilize reporting and analytics features. | Manage user permissions and access. | Contribute to knowledge base content creation. | Administrator Guide (PDF), Live Webinar, Dedicated Training Sessions |
Ongoing User Training and Support Plan
Ongoing training and support are essential for maintaining user proficiency and addressing evolving needs.Scheduled training sessions will be held monthly, covering topics such as new feature releases, advanced search techniques, and best practices for knowledge base utilization. Ongoing support will be provided through email, a dedicated help desk, and an online forum. User feedback will be collected through regular surveys and informal feedback channels to continuously improve the training program and address user concerns.
Post-Onboarding Quiz
This quiz assesses user understanding of key Bynder knowledge base functionalities.
1. Question
How do you access the Bynder knowledge base? Answer: Through the designated link/portal within the Bynder platform.
2. Question
What are the primary methods for searching for information? Answer: search, filtering by category, and using advanced search operators.
3. Question
How can you save frequently used articles? Answer: By using the “favorites” or “bookmark” function.
4. Question
How can you provide feedback on an article? Answer: Through a feedback form typically located at the bottom of each article.
5. Question
Where can you find information about user roles and permissions? Answer: In a dedicated section of the knowledge base or through the system’s administrative interface.
6. Question
What types of training resources are available? Answer: Video tutorials, interactive modules, PDF guides, FAQs, and live webinars.
7. Question
How can you report a problem or technical issue? Answer: Through the dedicated help desk or support channels.
User Feedback Mechanism
A structured survey will be used to gather user feedback on the training materials and onboarding process. The survey will include both quantitative (rating scales for satisfaction with various aspects) and qualitative (open-ended questions for detailed comments and suggestions) data collection methods. This feedback will be used to refine and improve the training program over time.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
This section addresses common problems users encounter while using the Bynder knowledge base and provides straightforward solutions. Understanding these common issues will help you quickly resolve any difficulties and maximize your efficiency. The solutions are presented in a frequently asked questions (FAQ) format for easy navigation.
Login Problems
Users may experience difficulties logging into the Bynder knowledge base. This can stem from several causes, including incorrect credentials, forgotten passwords, or browser-related issues.
- Incorrect Credentials: Double-check your username and password for typos. Ensure caps lock is off and that you’re using the correct account details provided during onboarding.
- Forgotten Password: Utilize the “Forgot Password” functionality within the login screen. Follow the instructions to reset your password via email.
- Browser Issues: Try clearing your browser’s cache and cookies. If the problem persists, try a different browser (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Edge).
Search Functionality Issues
Sometimes, users find the search function to be ineffective in locating the required information. This can be due to incorrect search terms or limitations in the search algorithm.
- Improper Search Terms: Use specific s related to your query. Experiment with different search terms and phrases. Try variations of the terms or synonyms.
- Search Algorithm Limitations: If you’re still unable to find the information, consider using the knowledge base’s navigation menu or browsing through the categorized sections.
Content Upload Issues
Uploading content to the Bynder knowledge base can sometimes present challenges. This could be related to file size limits, incompatible file formats, or network connectivity problems.
- File Size Limits: Check the knowledge base’s guidelines for maximum file sizes. Compress large files before uploading to ensure they meet the specified limits.
- Incompatible File Formats: Verify that the file format is supported by the Bynder knowledge base. Refer to the system requirements or contact support for clarification.
- Network Connectivity: Ensure a stable internet connection before uploading files. Intermittent connectivity can interrupt the upload process.
Permission Issues
Users might encounter issues accessing specific content or functionalities due to insufficient permissions.
- Insufficient Permissions: If you lack access to a particular feature or document, contact your administrator to request the necessary permissions. The administrator can adjust your user role to grant access.
Unable to Access Specific Content
Sometimes, users may find it difficult to locate or access specific information within the knowledge base.
- Outdated Information: The knowledge base is regularly updated. If you suspect the information is outdated, contact support to confirm the latest information.
- Incorrect Navigation: Double-check that you are navigating through the correct sections and sub-sections of the knowledge base.
Security and Access Control
Bynder’s knowledge base employs robust security measures to safeguard its content and ensure user data privacy. These measures are designed to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats, maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of the information stored within. Access control is meticulously managed to restrict sensitive information to only authorized personnel.Bynder utilizes a multi-layered security approach.
This includes robust firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. Data encryption both in transit and at rest further protects sensitive information. These safeguards are continuously monitored and updated to adapt to the evolving threat landscape.
User Access Management
User access to the Bynder knowledge base is controlled through a granular permission system. Each user is assigned a specific role, defining their level of access to different sections and functionalities. This role-based access control (RBAC) model ensures that only authorized personnel can view, edit, or delete specific information. For instance, administrators have full access, while standard users may only have read-only access to certain sections.
So you’re diving into Bynder’s knowledge base? That’s great! If you’re also working with youth and family programs, you might find the resources at the yfc knowledge base helpful as well. Both offer different perspectives, but together they can really boost your understanding. Remember to check both Bynder and the YFC resources for a complete picture.
This system allows for precise control over who can access what information, limiting the risk of unauthorized modifications or disclosures.
Security Incident Response
Bynder has established comprehensive procedures for handling security incidents related to the knowledge base. These procedures Artikel steps for identifying, containing, and remediating security breaches. A dedicated security team is responsible for investigating and responding to any security incidents promptly and effectively. Incident reporting mechanisms are in place to encourage users to report any suspicious activity. Regular security awareness training is provided to all users to enhance their understanding of security threats and best practices.
Following a security incident, a thorough post-incident review is conducted to identify areas for improvement and prevent similar incidents in the future. This includes reviewing security protocols and user access permissions to identify and address any vulnerabilities that may have been exploited. For example, if a phishing attempt was successful, the incident response team would analyze the attack, strengthen security measures against similar attacks (such as enhanced phishing detection), and re-train users on identifying and avoiding such threats.
Best Practices for Knowledge Base Articles
Creating effective knowledge base articles requires a strategic approach to content organization, writing style, and visual presentation. Well-structured articles not only answer user queries efficiently but also enhance user experience and contribute to a positive brand image. This section Artikels best practices for crafting high-quality, user-friendly knowledge base content.
Article Structure and Style
A clear and concise structure is crucial for effective knowledge base articles. Each article should begin with a brief, informative title that accurately reflects its content. Follow this with a concise introduction summarizing the article’s purpose and scope. Break down complex information into smaller, easily digestible sections using subheadings. Use bullet points or numbered lists for clarity when presenting multiple steps or options.
Maintain a consistent tone throughout the article, using plain language and avoiding jargon. Finally, conclude with a brief summary of key takeaways or next steps, if applicable. For example, an article explaining how to reset a password might start with a clear title, “Resetting Your Bynder Password,” then proceed with steps Artikeld using numbered lists, accompanied by screenshots depicting each step.
Visually Appealing and Digestible Content
Visual elements significantly enhance the readability and comprehension of knowledge base articles. Use short paragraphs, leaving ample white space between them to avoid overwhelming the reader. Incorporate bullet points and numbered lists to break up large blocks of text. Use headings and subheadings to create a clear visual hierarchy, guiding the reader through the information. Consistent font sizes and styles contribute to a clean and professional appearance.
Incorporating Images and Visual Aids
Images and other visual aids can dramatically improve understanding. For example, an article explaining the user interface could include a screenshot showing the location of a specific button or menu. This screenshot would depict a computer screen displaying the Bynder interface, with a clearly marked rectangle highlighting the “Upload” button, accompanied by a concise caption: “The Upload button is located in the top right corner of the screen.” Another example could be a flowchart illustrating a multi-step process, like submitting a request for access.
This flowchart would use distinct shapes and connecting arrows to visually represent the steps involved, each step labeled clearly. A third example could be a short animated GIF demonstrating how to perform a specific action, such as dragging and dropping a file into the Bynder system. This GIF would show a hand-like cursor smoothly moving a file icon from one designated area to another on the screen, accompanied by concise text describing the action.
Using the Bynder Knowledge Base for Internal Communication
Leveraging Bynder’s Knowledge Base effectively for internal communication streamlines information sharing, fosters collaboration, and enhances employee productivity. A well-structured and actively maintained knowledge base becomes a central hub for company-wide updates, policies, and best practices. This section details strategies for optimizing its use as an internal communication tool.
Content Strategy & Creation
Effective internal communication through the Bynder Knowledge Base requires a planned approach to content creation and management. This includes establishing a content calendar, defining clear content guidelines, and structuring the knowledge base for optimal searchability and user experience.
Content Calendar
A well-defined content calendar ensures consistent updates and relevant information for employees. The following table illustrates a sample content calendar for the next quarter. This calendar can be adapted and expanded upon to meet the specific needs of your organization.
| Date | Topic | Content Type | Target Audience | Author/Owner | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oct 26, 2023 | New Onboarding Process | Article | New Employees | HR Department | Scheduled |
| Nov 9, 2023 | Q4 Sales Targets | Video | Sales Team | Sales Manager | In Progress |
| Nov 23, 2023 | Updated IT Security Protocols | Article & FAQ | All Employees | IT Department | To Do |
| Dec 7, 2023 | Holiday Schedule & Office Closure | Article | All Employees | HR Department | Scheduled |
Content Guidelines
Consistent style and formatting are crucial for a user-friendly knowledge base. Guidelines should cover aspects such as heading styles (using H2, H3, etc. consistently), image formatting (size, captions, alt text), link formatting (clear and descriptive anchor text), and a consistent brand voice (professional yet approachable). These guidelines should be readily accessible to all contributors. For example, headings should follow a clear hierarchical structure (H2 for main sections, H3 for subsections, etc.), and all images should include descriptive alt text for accessibility.
Knowledge Base Structure
A logical structure is key to easy navigation. A hierarchical structure, organized by department, topic, or workflow, is recommended. For instance, a tree diagram could start with broad categories like “Marketing,” “Sales,” “HR,” and then branch out into more specific s within each category. This allows users to quickly find the information they need. A visual representation of this structure (e.g., a flowchart or sitemap) would be beneficial for users and contributors alike.
Employee Engagement & Participation
Encouraging active participation from employees is vital for a dynamic and up-to-date knowledge base. Gamification and effective training can significantly boost contributions.
Gamification
A points-based system, where employees earn points for creating, updating, or improving articles, can incentivize participation. Leaderboards displaying top contributors and badges recognizing specific achievements (e.g., “Most Helpful Article,” “Top Contributor”) can further enhance engagement. Points could be redeemed for rewards, such as gift cards or extra vacation time.
Training & Onboarding
A short, interactive training module, incorporating videos and screen recordings, will guide employees on creating and editing articles, using tags and metadata, and understanding the knowledge base’s structure. This training should be readily accessible and easily repeatable.
Feedback Mechanism
A dedicated feedback form or section within each article allows users to provide suggestions for improvements. Regular surveys assessing user satisfaction and usability can further inform content updates and improvements. Analyzing this feedback is crucial for continuous improvement.
Measurement & Reporting
Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) provides valuable insights into the knowledge base’s effectiveness.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
KPIs should include metrics such as page views, search queries, user engagement (time spent on page, bounce rate), and employee satisfaction scores (measured through surveys). These metrics offer a comprehensive view of the knowledge base’s performance and user experience.
Reporting Dashboard
A dashboard visualizing these KPIs, using charts and graphs, will allow for quick identification of trends and areas for improvement. For example, a sample dashboard could display the number of page views per article, the most frequently searched terms, and the average user satisfaction score. This dashboard should be accessible to relevant stakeholders.
Advanced Features
Integrating the Bynder Knowledge Base with other systems and implementing robust version control can enhance its functionality.
Integration with other systems
Integrating the Bynder Knowledge Base with the HRIS system could automate the onboarding process by providing new employees with access to relevant knowledge base articles. Integration with project management software could streamline access to project-related documentation.
Version Control and Workflow
A clear workflow for managing revisions, including a formal approval process, prevents conflicting edits and ensures the accuracy of information. A flowchart outlining the steps involved in submitting, reviewing, and approving updates is crucial for efficient workflow management. This might include stages like submission, review by a designated editor, approval by a manager, and final publication.
Measuring the Effectiveness of the Bynder Knowledge Base
A successful Bynder knowledge base significantly reduces support tickets, empowers users to solve problems independently, and fosters a more efficient work environment. Measuring its effectiveness requires a multi-faceted approach, tracking key metrics and actively soliciting user feedback. This allows for continuous improvement and ensures the knowledge base remains a valuable resource.Key Metrics for Evaluating SuccessUnderstanding the knowledge base’s impact requires tracking several key performance indicators (KPIs).
These metrics provide quantifiable data illustrating its effectiveness and areas needing attention.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Several key metrics can illuminate the effectiveness of the Bynder knowledge base. These metrics offer a comprehensive view of user engagement and knowledge base impact. Tracking these over time allows for identifying trends and areas for improvement.
- Search Success Rate: The percentage of users who find the information they need through a search. A high success rate indicates well-organized and easily searchable content. A low rate might suggest poor indexing, unclear terminology, or missing information.
- Average Time on Page: The average time spent on a knowledge base article. A longer average time could indicate comprehensive and helpful content, while a short time might point to unclear or insufficient information.
- Number of Support Tickets: A decrease in support tickets related to issues addressed in the knowledge base is a strong indicator of its effectiveness. This directly reflects the reduction in reliance on support staff for common issues.
- Knowledge Base Article Views: The total number of times knowledge base articles are viewed. High view counts indicate users are actively utilizing the resource. Analyzing which articles are viewed most frequently can highlight popular topics and areas needing further development.
- User Satisfaction Scores: Feedback surveys or ratings associated with specific articles or the overall knowledge base experience. This provides direct user input on the helpfulness and clarity of the content.
Gathering User Feedback
Direct user feedback is crucial for understanding the knowledge base’s strengths and weaknesses from the user’s perspective. Implementing various feedback mechanisms allows for a comprehensive understanding of user needs and experiences.
- Post-Search Surveys: Brief surveys presented after a user completes a search, asking about the ease of finding the information and the relevance of the results.
- Embedded Feedback Forms: Forms within each article allowing users to rate the article’s helpfulness and provide comments or suggestions.
- Regular User Interviews: Conducting interviews with a representative sample of users to gain deeper insights into their experience and identify areas for improvement.
- Support Ticket Analysis: Examining support tickets to identify recurring questions or issues that could be addressed through improved knowledge base content.
Using Feedback for Improvement
Analyzing collected feedback is vital for refining the knowledge base and making it more user-friendly and effective. This iterative process ensures continuous improvement and enhances the overall user experience.
- Content Updates: Based on feedback, update existing articles to improve clarity, accuracy, and completeness. Address specific user concerns and incorporate suggestions for improvement.
- New Article Creation: Identify gaps in the knowledge base based on frequently asked questions or recurring support issues. Create new articles to address these gaps and provide comprehensive information.
- Navigation Improvements: Based on user feedback regarding navigation challenges, improve the knowledge base’s structure and search functionality to enhance usability.
- Search Optimization: Refine search terms and indexing to improve search results relevance. This may involve updating s or using more sophisticated search algorithms.
Future Developments and Enhancements
The Bynder knowledge base, while currently robust, possesses significant potential for future growth and improvement. By incorporating emerging technologies and addressing user feedback, we can enhance its functionality, usability, and overall effectiveness as a central resource for Bynder users. This section Artikels potential future developments and enhancements, focusing on concrete feature proposals, technology integration, and user experience optimization.
Specific Feature Proposals
Three concrete new features are proposed to enhance the Bynder knowledge base, addressing current limitations and unmet user needs.
- Personalized Recommendations: This feature would leverage user activity and search history to suggest relevant articles and resources proactively. This personalized approach would improve information discovery and reduce search time. For example, a user frequently searching for “asset management” would be presented with related articles on DAM best practices and workflow optimization before initiating a search. The justification for this is to improve user experience and efficiency by providing more targeted information.
- Collaborative Article Editing: This feature would allow multiple users to simultaneously edit a single knowledge base article, facilitating faster updates and improved content quality. This would be particularly beneficial for large teams managing content collaboratively. For instance, a team of writers could work concurrently on updating a product manual, reducing the time required for revisions and streamlining the update process.
The justification for this feature is to streamline workflow and enhance content collaboration.
- Advanced Search with Semantic Understanding: This feature would enhance the current search functionality by incorporating natural language processing (NLP) to understand user intent better. This would enable more accurate search results even with less precise search terms. For example, a user searching for “how to upload images” might also receive results on “uploading videos” or “managing assets,” as the system understands the underlying intent.
This would improve search accuracy and the user experience significantly. The justification is to enhance search accuracy and improve user experience.
Prioritization Matrix
The following matrix prioritizes the proposed features based on feasibility and impact.
| Feature | Feasibility | Impact | Justification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personalized Recommendations | High | High | Relatively straightforward implementation using existing user data; significant impact on user experience and efficiency. |
| Collaborative Article Editing | Medium | High | Requires more complex development to manage concurrent edits and version control; high impact on content creation and update speed. |
| Advanced Search with Semantic Understanding | Low | High | Requires integration of NLP technology and significant development effort; potentially very high impact on search accuracy and user satisfaction. |
Emerging Technologies for Enhancement
Three emerging technologies can significantly enhance the Bynder knowledge base.
- AI-Powered Search: Implementing an AI-powered search engine would drastically improve search accuracy and relevance. This could involve using machine learning algorithms to understand user queries better and provide more precise results, even with ambiguous or incomplete search terms. This would be integrated by replacing the current search engine with an AI-powered alternative, trained on the existing knowledge base content.
Improved search accuracy and reduced search time are the expected outcomes. A potential challenge is the need for high-quality training data and ongoing maintenance of the AI model.
- Virtual Assistants: Integrating a virtual assistant could provide users with instant access to information through natural language interactions. Users could ask questions in plain language, and the virtual assistant would retrieve relevant articles or provide guidance. This could be integrated through a chat interface on the knowledge base platform. Improved accessibility and user engagement are expected. A potential challenge is ensuring the virtual assistant accurately understands and responds to a wide range of user queries.
- Personalized Learning Paths: This would involve creating tailored learning paths based on user roles and needs. Users would receive targeted recommendations for articles and tutorials relevant to their specific tasks and responsibilities. This would be implemented by analyzing user roles and creating customized content pathways. Improved onboarding and training efficiency are expected. A potential challenge is the effort required to create and maintain these personalized learning paths.
Areas for UX/UI Optimization
A brief UX/UI audit reveals three areas for improvement.
- Improved Navigation: The current navigation structure could be simplified and made more intuitive, potentially using a hierarchical structure or a faceted navigation system to help users locate information more easily.
- Enhanced Search Functionality: Adding advanced search filters (e.g., date range, article type, author) and implementing autosuggestions would improve the search experience.
- Improved Information Architecture: A thorough review of the knowledge base’s content organization is needed to ensure articles are logically grouped and easily discoverable. This may involve reorganizing categories and subcategories to improve information findability.
Efficiency Improvements
Three strategies can improve knowledge base efficiency.
- Automated Content Updates: Automating the update of frequently changing information (e.g., software version numbers) will save time and ensure accuracy.
- Content Versioning and Rollback: Implementing a robust version control system allows for easy tracking of changes and enables quick rollback to previous versions if needed.
- Template-Based Article Creation: Creating templates for common article types can standardize content formatting and speed up the creation process.
User Feedback Integration
A systematic approach to gathering and incorporating user feedback is crucial. This would involve:
- Surveys: Regularly sending out short surveys to users to gather feedback on their experience.
- Feedback Forms: Including feedback forms within the knowledge base itself to allow for immediate feedback.
- User Interviews: Conducting user interviews to gather more in-depth feedback and insights.
- Data Analytics: Tracking key metrics (e.g., search queries, article views, user engagement) to identify areas for improvement.
The feedback gathered would be analyzed, prioritized based on impact and feasibility, and used to inform improvements to the knowledge base’s UX and efficiency.
Query Resolution
Can I customize the look and feel of the Bynder Knowledge Base?
Absolutely! Bynder offers various customization options to align the knowledge base with your brand’s aesthetic and ensure a consistent user experience.
How do I get support if I encounter issues with the Bynder Knowledge Base?
Bynder provides comprehensive support channels, including detailed documentation, online tutorials, and dedicated customer support teams ready to assist you.
What types of files can I upload to the Bynder Knowledge Base?
You can upload a wide range of file types, including documents, images, videos, and more. The specific file types supported might depend on your Bynder configuration.
Is the Bynder Knowledge Base mobile-friendly?
Yes! The Bynder Knowledge Base is designed to be responsive and accessible across various devices, including desktops, tablets, and smartphones, ensuring a consistent user experience regardless of the device.
Can I integrate the Bynder Knowledge Base with my existing helpdesk system?
Depending on your helpdesk system, integration may be possible through APIs or other methods. Check Bynder’s integration documentation for compatibility details and instructions.


